Robotics in Manufacturing & Factories
The modern factory floor is undergoing a paradigm shift from rigid assembly lines to flexible, autonomous production ecosystems. Robotics in manufacturing is no longer just about heavy lifting; it is about precision, interconnectivity, and the seamless orchestration of Industry 4.0 standards.
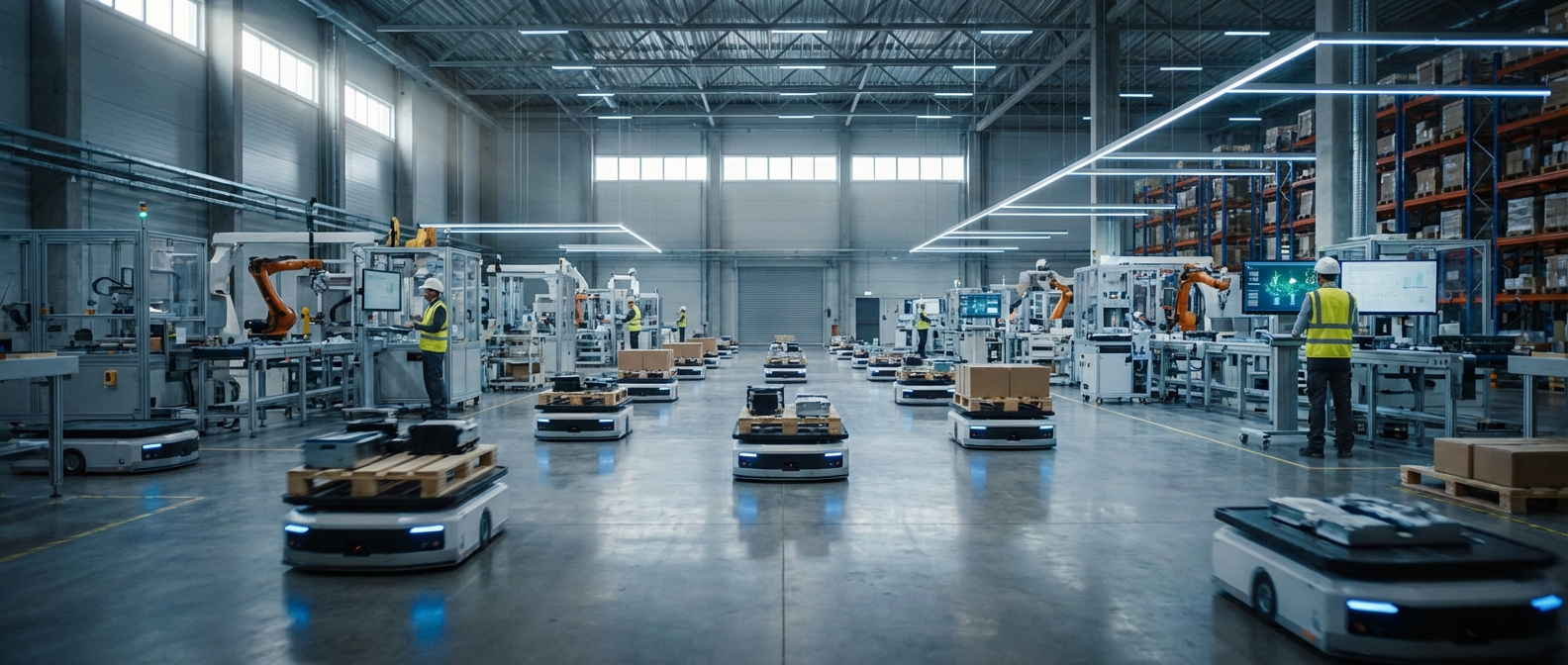

Why Robotics Matters Here
Addressing Labor Shortages
Factories face a global shortage of skilled manual labor. Robots fill critical gaps, handling repetitive tasks 24/7 without fatigue, allowing human workers to focus on supervision and complex problem-solving.
Precision & Consistency
Human error is inevitable in high-volume production. Robotic systems maintain micron-level tolerance over millions of cycles, drastically reducing waste and ensuring uniform product quality.
Worker Safety
Manufacturing environments often involve heavy lifting, toxic fumes, or extreme temperatures. Robots take over "the dull, the dirty, and the dangerous," reducing workplace injuries and liability.
Production Agility
Consumer demand changes rapidly. Modern cobots and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) can be reprogrammed and redeployed in hours, not weeks, enabling "high mix, low volume" manufacturing.
Operational Efficiency
Throughput is the key metric of factories. Automation optimizes flow efficiency, reduces bottlenecks in material transport, and ensures that assembly lines run at optimal takt time.
Data-Driven Insights
Smart robots act as IoT endpoints. They collect real-time data on production metrics and equipment health, enabling predictive maintenance that prevents costly unplanned downtime.
Applications in Manufacturing & Factories
Welding Automation
Learn how welding automation transforms manufacturing & factories through consistent arc control and speed.
Explore Application →Assembly Line Transport
Learn how assembly line transport transforms manufacturing & factories using AMRs to move materials dynamically.
Explore Application →Inspection & Monitoring
Learn how inspection & monitoring transforms manufacturing & factories via high-speed vision systems.
Explore Application →How to Deploy Robotics in Your Factory
Implementing automation is not a "plug and play" operation; it is a strategic transformation. The journey begins with a comprehensive Site Assessment. We identify bottlenecks where manual intervention causes variability—typically in end-of-line packaging or inter-process logistics—and calculate the potential ROI based on labor savings and throughput increase.
Next is Integration and Simulation. Before a single physical robot is deployed, we utilize Digital Twins to simulate the cell in your virtual environment. This ensures that reach studies, cycle times, and safety zones are optimized without disrupting current operations.
Finally, we focus on Upskilling and Scaling. Successful deployment requires the buy-in of your workforce. We provide training to transition operators into "robot pilot" roles, and once the pilot cell hits KPIs, we scale the solution horizontally across your facility.
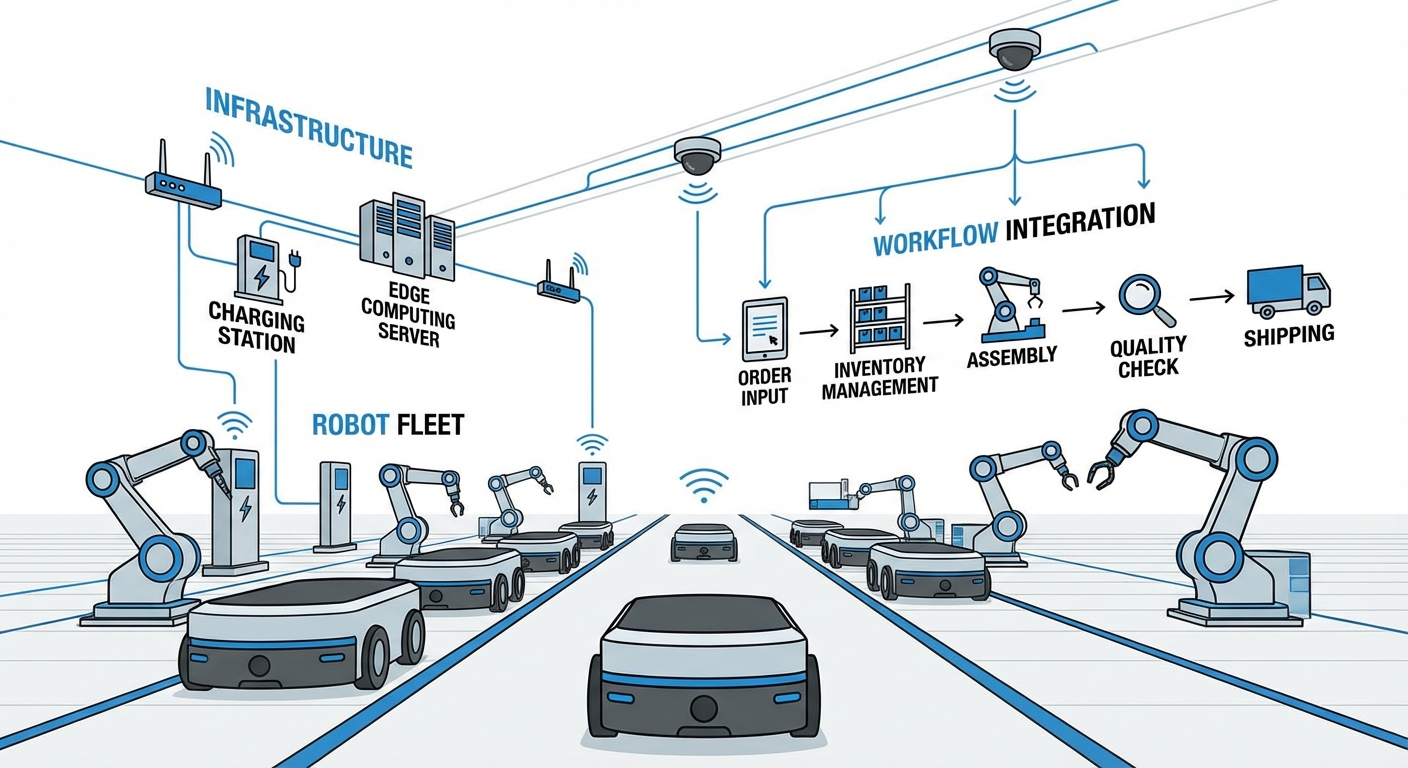
Success Stories
Reducing Cycle Time by 40%
Challenge: An auto-parts manufacturer struggled with inconsistent manual spot welding, leading to a high rejection rate.
Solution: Deployed a cell of 6-axis robotic arms synchronized with a rotary table.
Result: 40% faster production and near-zero defects.
Precision Micro-Assembly
Challenge: Assembling microscopic PCB components caused high eye-strain and fatigue for workers.
Solution: Implementation of high-speed SCARA robots with machine vision guidance.
Result: 99.9% yield rate and improved staff retention.
Autonomous Material Transport
Challenge: Forklift traffic in the warehouse created safety hazards and logistical bottlenecks.
Solution: A fleet of heavy-payload AMRs to transport raw steel between machining centers.
Result: Eliminated forklift accidents and optimized inventory flow.
End-of-Line Palletizing
Challenge: Manual palletizing was a bottleneck preventing the packaging line from running at full speed.
Solution: Collaborative palletizing robots working alongside humans to stack boxes.
Result: 25% increase in total line throughput.
Industry-Specific Questions
What is the typical ROI timeframe for manufacturing robotics?
While this varies by application, most factories achieve ROI in 12 to 24 months. Factors include labor savings, reduction in scrap materials, and the ability to run lights-out shifts (24/7 production).
Can robots work with our legacy machines (Brownfield integration)?
Yes. Modern robotics can integrate with legacy equipment using retrofitted sensors and PLCs. We often use digital I/O modules to allow new robots to communicate with older CNC machines or conveyors without replacing the entire line.
How do we handle safety in shared workspaces?
Safety is managed via ISO 10218 and ISO/TS 15066 standards. Solutions range from physical caging for high-speed industrial robots to force-limiting sensors and LIDAR safety scanners for collaborative robots (cobots) that slow down or stop when humans approach.
What maintenance do industrial robots require?
Routine maintenance includes greasing joints, checking cable harnesses, and updating software. However, predictive maintenance using vibration and thermal sensors allows us to service robots only when necessary, preventing unplanned downtime.
Are these robots difficult to program?
The industry is moving toward "low-code" or "no-code" interfaces. Many modern cobots use lead-through programming (moving the arm by hand to teach waypoints), making them accessible to factory floor operators without advanced coding skills.
How do robots handle high-mix, low-volume production?
We utilize flexible end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) like adaptive grippers or tool changers. Combined with vision systems that can recognize different parts, a single robot cell can switch between product lines in minutes.
Can robots operate in dirty or hazardous environments?
Absolutely. We specify robots with appropriate IP ratings (e.g., IP67) for dust and water resistance. Foundry-grade robots are designed to withstand extreme heat and metal splash, protecting them in environments unsafe for humans.
How does this impact our power consumption?
While adding machinery increases load, robots are highly efficient. They optimize movement paths to conserve energy and can work in unlit and unheated environments (HVAC savings), often resulting in a net-neutral or positive energy impact per unit produced.
What about cybersecurity risks?
As IIoT devices, robots are secured through network segmentation, encrypted communication protocols (like OPC UA), and strict access controls. We ensure all deployments comply with IEC 62443 cybersecurity standards.
Can we lease robots instead of buying (RaaS)?
Yes, Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) is becoming popular. It shifts the cost from CAPEX to OPEX, allowing you to pay a monthly fee or per-pick rate, which includes maintenance and upgrades.