Welding Automation
Revolutionize your production line with high-precision robotic welding solutions. Enhance weld quality, significantly reduce cycle times, and remove operators from hazardous environments while ensuring consistent repeatability.
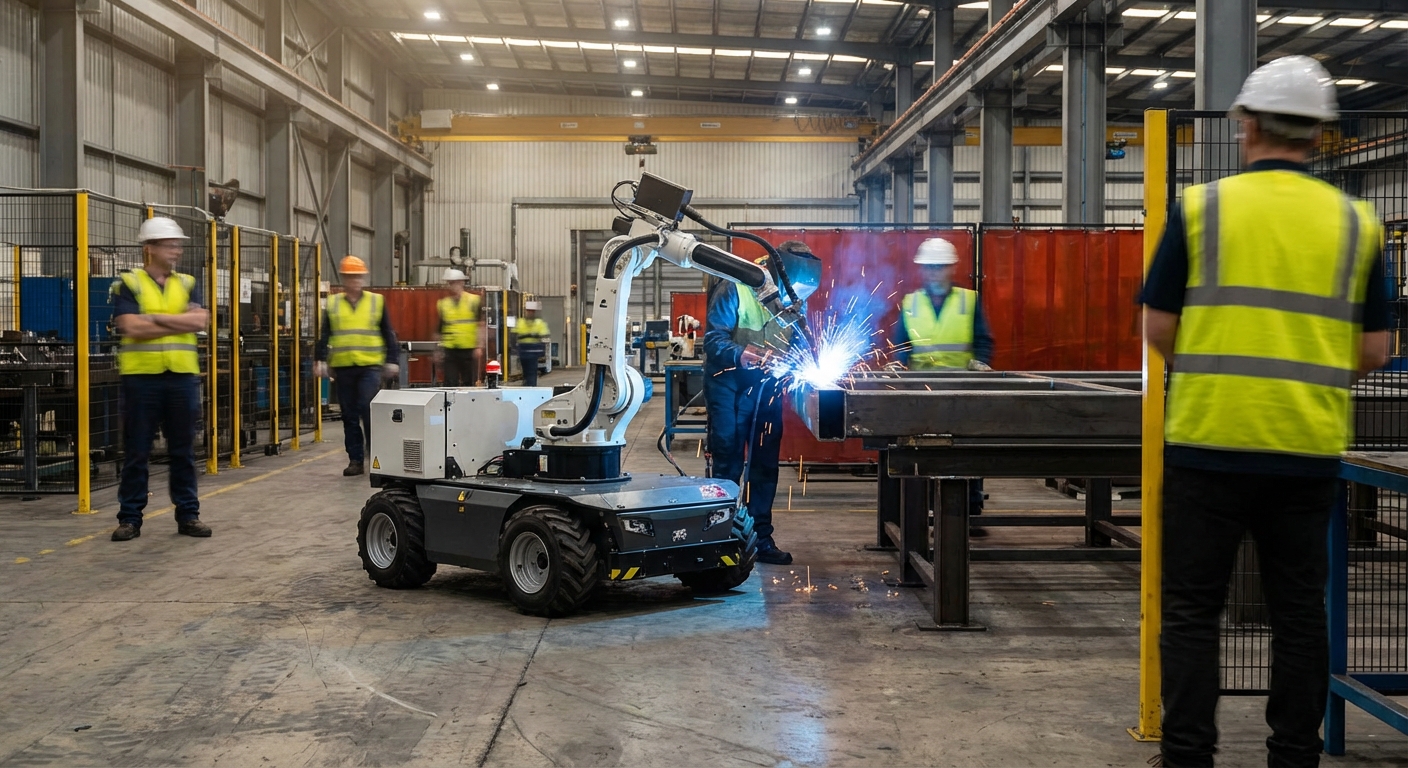

Why Automate Welding?
Pinpoint Accuracy
Robots deliver tolerance levels within fractions of a millimeter, ensuring every weld is placed exactly where required.
Enhanced Safety
Protect workers from toxic fumes, flash burns, and repetitive strain injuries by offloading dangerous tasks to automation.
Increased Throughput
Robots work tirelessly without breaks, significantly increasing parts-per-hour and reducing production bottlenecks.
Material Efficiency
Precise control over wire feed and arc time reduces consumables waste and minimizes post-weld cleanup.
Unwavering Consistency
Eliminate human variability. Every part produced at 8:00 AM matches the quality of parts produced at 5:00 PM.
Lower Labor Costs
Shift skilled labor to supervisory roles and reduce costs associated with hiring for difficult-to-fill manual welding positions.
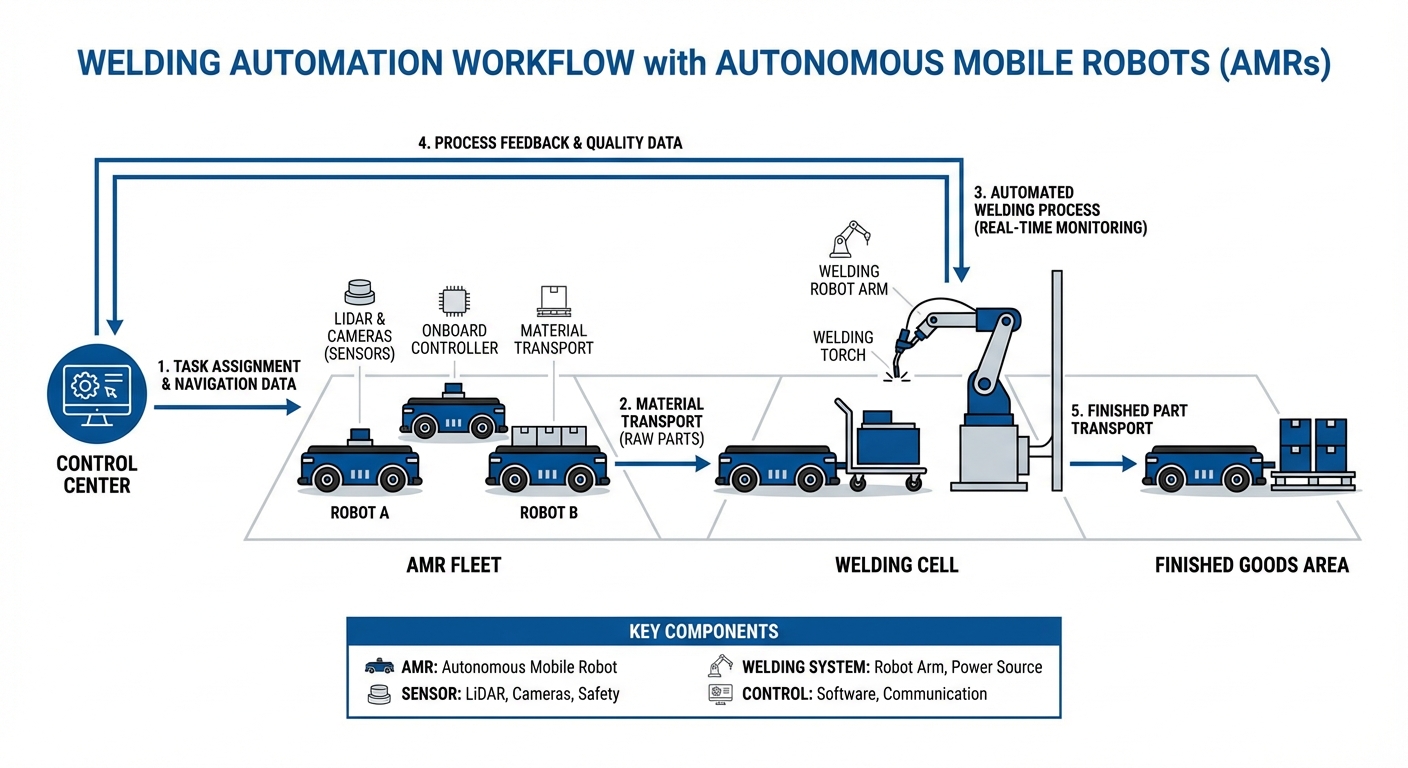
Technical Implementation
The process begins with Path Programming. Using either teach pendants or offline simulation software, the robot's trajectory is mapped relative to the workpiece. Advanced systems utilize 3D vision to locate the part, compensating for slight fixture misalignments.
During the Execution Phase, the robot arm coordinates with the welding power source. It precisely controls travel speed, voltage, wire feed rate, and weave patterns. Real-time seam tracking sensors adjust the robot's path on the fly if thermal distortion occurs.
Finally, the cycle concludes with Quality Assurance. Integrated sensors monitor arc data to detect porosity or burn-through instantly. The system can automatically reject defective parts or alert operators for inspection, ensuring only perfect products leave the cell.
Where It's Used
Automotive Manufacturing
Used extensively for chassis assembly, spot welding body panels, and exhaust system fabrication where high speed and volume are critical.
Heavy Machinery
Ideal for long, multi-pass welds required in the production of excavators, tractors, and mining equipment, reducing operator fatigue.
Structural Steel
Automates the joining of beams and trusses for construction, ensuring structural integrity and meeting strict building codes.
Energy & Pipelines
Provides high-quality orbital welding for pipelines and pressure vessels, critical for preventing leaks in high-pressure environments.
What You Need
| Component category | Requirements & Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Robot Arm | 6-axis industrial manipulator with appropriate payload (5kg - 50kg+) and reach capabilities (1.4m - 3m). High path accuracy/repeatability (±0.05mm). |
| Welding Equipment | Digital power source (MIG/MAG/TIG) with robot interface capabilities (Fieldbus/Ethernet). Liquid-cooled torch for high duty cycles. |
| Sensors & Vision | Touch sensing (tactile) or Laser Seam Tracking for part location. Through-Arc Seam Tracking for real-time path correction. |
| Safety Systems | Safety PLCs, light curtains, perimeter fencing, and fume extraction units compliant with OSHA/ISO standards. |
| Software | Offline programming software (OLP) to minimize downtime; Welding parameter monitoring software for QA. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Which welding processes can be automated?
Almost all standard processes can be automated, including MIG/MAG (GMAW), TIG (GTAW), Spot Welding (RSW), Laser Welding, and Plasma welding. MIG is the most common due to its versatility and speed.
Is robotic welding suitable for small batches?
Yes, specifically with modern Offline Programming (OLP) tools and "Cobots" (Collaborative Robots). These allow for rapid reprogramming, making high-mix/low-volume production economically viable.
How do robots handle gaps or poor fit-up?
Standard robots blindly follow a path. However, by integrating Laser Seam Tracking or Through-Arc Sensing, the robot can detect variations in the joint gap and adjust the weave pattern or travel speed in real-time to fill the gap.
What is the typical ROI period?
Return on Investment varies, but most manufacturing facilities see a full ROI between 12 to 24 months, driven by reduced scrap, lower labor costs, and increased daily output.
Do I need to hire a specialized programmer?
Not necessarily. Modern robot interfaces are increasingly user-friendly (drag-and-drop or hand-guiding). However, existing welders should be trained to operate the robot, leveraging their welding knowledge for parameter tuning.
How safe are welding robots?
They are very safe when properly integrated. Cells are typically enclosed with safety fencing and light curtains. Fume extraction systems are more efficient as they can be mounted directly at the source (the torch tip).
What maintenance is required?
Routine maintenance includes changing torch consumables (contact tips, nozzles), cleaning wire liners, checking TCP (Tool Center Point) alignment, and standard robot greasing intervals (usually annual).
Can existing manual fixtures be used?
Sometimes, but often they need modification. Robotic fixtures must be more precise and offer better repeatability than manual ones. They also need to provide clearance for the robot torch to access the joint angles.
Does it work with aluminum?
Yes. Robotic welding is actually excellent for aluminum because the precise speed control helps manage heat input, reducing the risk of burn-through on thin materials.
What is a positioner and do I need one?
A positioner rotates the workpiece while the robot welds. It is highly recommended for complex parts to ensure the robot can always weld in the "flat" or horizontal position, which yields the strongest welds.