Robotics in Education & Research
The academic landscape is shifting from theoretical abstraction to hands-on interaction. Advanced robotics provide the tangible platform needed to bridge the gap between complex algorithms and real-world physical behavior, accelerating discovery in labs and engagement in classrooms.

Why Robotics Matters Here
Bridging Theory & Practice
Students struggle to visualize complex kinematic theories. Robots provide immediate physical feedback for coding and mechanical engineering concepts.
Lab Safety & Consistency
Handling hazardous materials or repetitive pipetting leads to risk and error. Automation ensures safety and 100% repeatability in experiments.
Data Precision
Human observation introduces bias. Robotics integrated with sensors collect granular, objective data sets critical for publishing peer-reviewed results.
Open Source Ecosystems
Proprietary systems lock researchers out. Our platforms support ROS 2 and Python, allowing full access to modify control loops and algorithms.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Modern problems require team-ups. Robotics brings Computer Science, Mechanical Engineering, and Biology departments together on a single platform.
Remote Labs
Distance learning lacks hands-on labs. Telepresence robots allow remote students to manipulate hardware and run experiments from anywhere.
Applications in Education & Research
Educational Research Platform
Learn how educational research platform transforms education & research by providing flexible, code-agnostic foundations.
Explore Application →Laboratory Sample Transport
Learn how laboratory sample transport transforms education & research through autonomous intra-logistics and secure chain of custody.
Explore Application →Inspection & Monitoring
Learn how inspection & monitoring transforms education & research by automating environmental data collection and facility safety checks.
Explore Application →How to Deploy
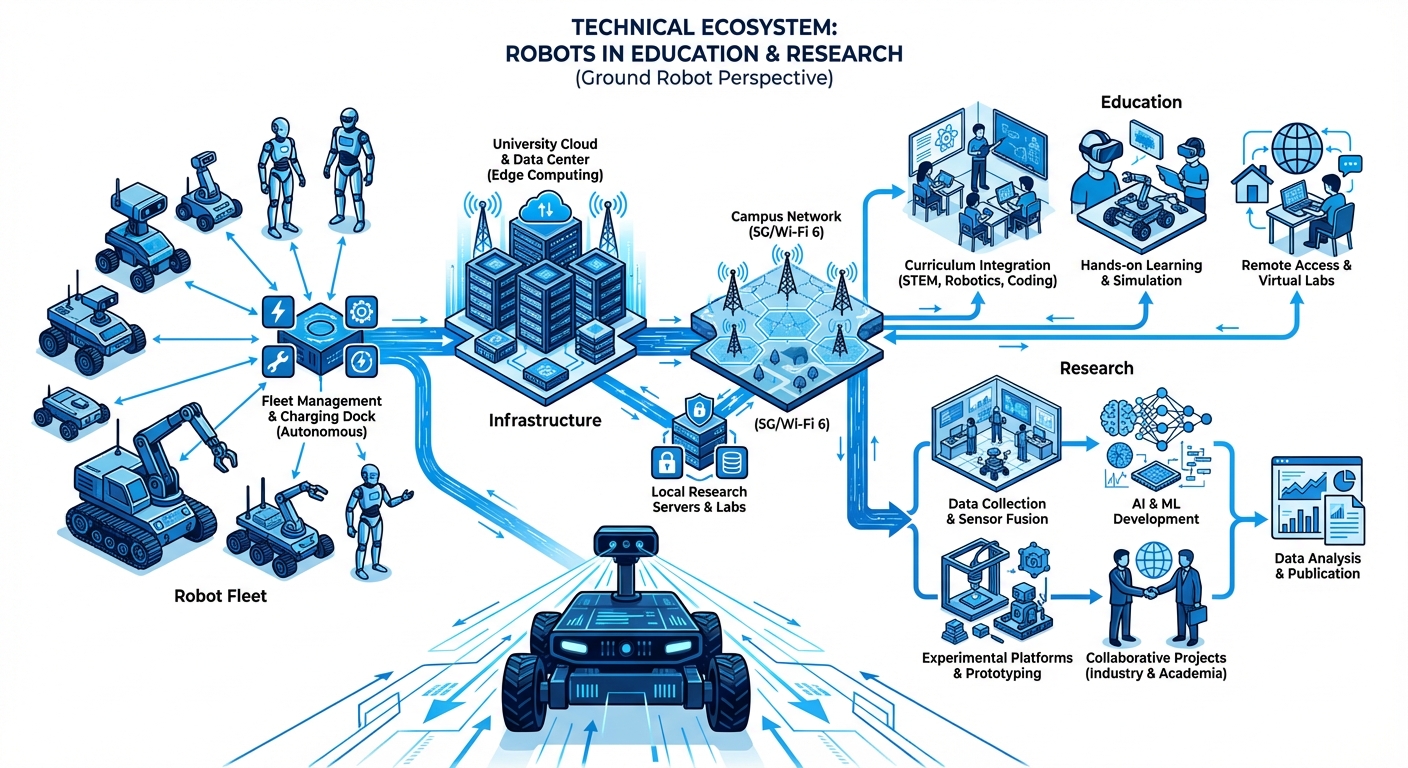
Implementing robotics in an educational or research setting requires a balance between accessibility for students and rigor for researchers. The first step is defining the Curriculum & Research Goals. Determine if the focus is on low-level control theory (requiring open hardware APIs) or high-level AI application (requiring robust simulation environments).
Next, focus on Infrastructure & Safety. Establish designated operating zones, whether they are enclosed arenas for aerial drones or flat terrain for AMRs. Our systems come with built-in collision avoidance and emergency stops, but physical boundaries ensure an extra layer of safety during early-stage student programming.
Finally, integrate via Middleware & Scalability. We recommend utilizing ROS 2 (Robot Operating System) as the backbone. This allows you to start with a single unit for a pilot study and scale to a fleet swarm for complex multi-agent research without rewriting your codebase.
Success Stories
Democratizing Reinforcement Learning
Challenge: Students could only test RL models in simulation due to the high cost of durable robot hardware.
Solution: Deployed 10 ruggedized AMRs with NVIDIA Jetson cores.
Result: 300% increase in published papers; students successfully transferred Sim-to-Real models within a single semester.
24/7 Automated Sample Handling
Challenge: Human error in transporting volatile samples between cold storage and testing units.
Solution: Integrated a mobile manipulator with existing LIMS software.
Result: Zero sample spoilage over 12 months; researchers reclaimed 15 hours/week from manual transport tasks.
Precision Phenotyping
Challenge: Manually measuring crop growth in large fields was slow and inconsistent.
Solution: All-terrain rovers equipped with multispectral cameras and LiDAR.
Result: Data collection speed increased by 10x; enabled micro-climate analysis previously impossible manually.
Workforce Readiness
Challenge: Local manufacturing partners needed technicians skilled in maintenance, not just coding.
Solution: Hands-on curriculum using modular, industrial-grade service robots.
Result: 95% placement rate for graduates in high-paying mechatronics roles.
Industry-Specific Questions
Do your robots support ROS / ROS 2?
Yes, all our research platforms are fully compatible with ROS 1 (Noetic) and ROS 2 (Humble/Iron). We provide official packages, URDF models, and simulation environments to ensure seamless integration into your existing curriculum or research stack.
Are these robots safe for undergraduate student use?
Safety is a priority. Our robots feature multi-layer safety systems, including physical E-stops, LiDAR-based collision avoidance, and software-imposed velocity limits. We recommend training sessions, but the hardware is designed to be forgiving of student programming errors.
Can we attach custom sensors or payloads?
Absolutely. Our platforms feature industry-standard mounting rails (extruded aluminum profiles) and accessible power ports (5V, 12V, 24V) specifically designed for researchers to mount custom LiDARs, robotic arms, depth cameras, or biological sampling equipment.
Do you offer educational discounts?
Yes, we offer tiered pricing for accredited educational institutions and research grants. Please contact our sales team with your .edu email address or grant details for specific quote adjustments.
What programming languages are supported?
Primary support is for Python and C++. However, because our systems utilize standard TCP/IP communication and REST APIs, you can interface with the robots using MATLAB, Java, or LabVIEW depending on your department's preference.
Is simulation software included?
We provide full digital twins for Gazebo and NVIDIA Isaac Sim. This allows students to write and test code in a virtual environment before deploying it to the physical robot, protecting hardware and speeding up class throughput.
How durable are the robots for outdoor research?
We have specific models rated IP54 to IP65 for outdoor use. These are designed to handle varying terrains like grass, gravel, and asphalt, making them ideal for agricultural or environmental research projects.
Can multiple robots communicate (Swarm Robotics)?
Yes. Our networking stack supports multi-agent systems out of the box. You can configure a fleet management server or use peer-to-peer communication for research into swarm intelligence and decentralized control algorithms.
What is the battery life for field experiments?
Depending on the payload and terrain, our research robots typically offer 4 to 8 hours of continuous runtime. Batteries are hot-swappable to ensure zero downtime during extended field data collection sessions.
Do you provide curriculum materials?
We provide a "Getting Started" guide and sample code repositories that cover navigation, mapping (SLAM), and object recognition. While we don't provide a full semester syllabus, our materials are designed to be easily adapted into existing robotics courses.