Zigbee Communication
Revolutionize your AGV fleet connectivity with the industry standard for low-power, self-healing mesh networking. Zigbee ensures continuous, reliable communication between mobile robots and control systems in complex industrial environments where traditional Wi-Fi fails.

Core Concepts
Mesh Topology
Unlike point-to-point connections, Zigbee devices route data through neighboring nodes. If an AGV is blocked, the signal finds an alternative path instantly.
Ultra-Low Power
Designed for efficiency, Zigbee allows sensor nodes and peripheral robotics hardware to operate for years on standard batteries without maintenance.
AES-128 Security
Industrial automation requires robust security. Zigbee implements 128-bit symmetric encryption to prevent unauthorized command injection.
Interference Avoidance
Operating on the 2.4 GHz band, Zigbee utilizes Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and channel agility to maintain integrity in noisy factories.
Massive Scalability
A single Zigbee network can theoretically support up to 65,000 nodes, making it ideal for massive warehouse swarms and sensor arrays.
Standardized Protocol
Built on IEEE 802.15.4, Zigbee ensures interoperability between different hardware vendors, preventing vendor lock-in for your robotic components.
How Zigbee Drives AGVs
In a typical industrial robotics setup, Zigbee functions through three specific device types: the Coordinator, Routers, and End Devices. The Coordinator initiates the network and stores security keys, typically integrated into the central Warehouse Management System (WMS).
AGVs usually act as Routers. This is the critical advantage: every robot in your fleet acts as a signal repeater. As Robot A moves to the far corner of a warehouse, it can relay telemetry data through Robot B and Robot C back to the central controller.
This dynamic "self-healing" capability means that if a forklift blocks a direct signal path, or if one node goes offline, the network automatically re-routes packets instantly, ensuring zero downtime for critical fleet coordination.
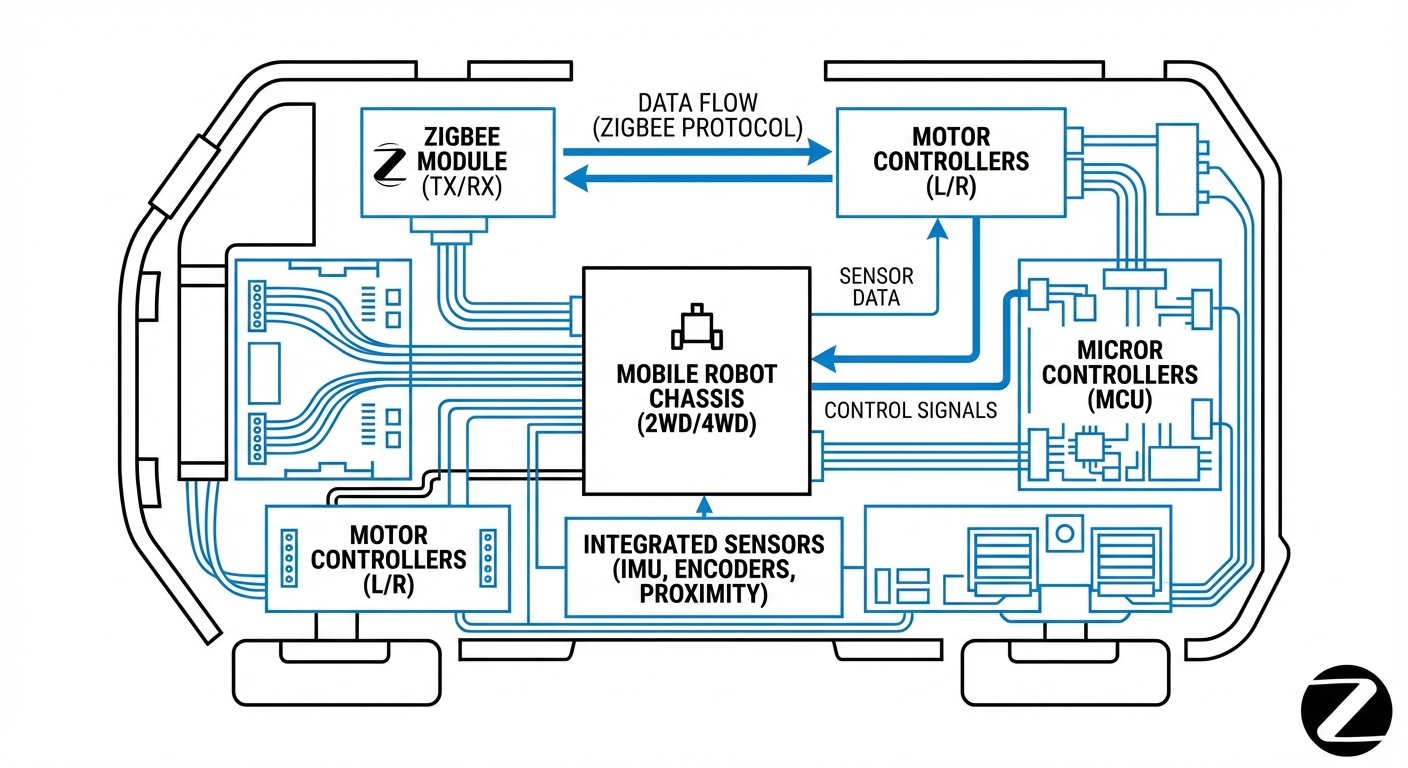
Real-World Applications
Warehouse Swarm Coordination
In fulfillment centers, hundreds of Kiva-style robots use Zigbee to maintain relative positioning and receive picking instructions without congesting the high-bandwidth Wi-Fi used by human workers.
Industrial IoT Sensor Integration
AGVs equipped with Zigbee can collect data from environmental sensors (temperature, humidity, vibration) placed on machinery as they pass by, uploading data to the central cloud.
Hospital Logistics Robots
Delivery robots in hospitals utilize Zigbee to communicate with automated doors and elevators, ensuring seamless vertical and horizontal transport of linens and medicine.
Asset Tracking & Geofencing
Zigbee nodes placed on pallets and inventory allow AGVs to locate specific items via triangulation (RSSI), providing granular inventory visibility within the facility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between Zigbee and Wi-Fi for robotics?
The primary difference lies in power consumption and data rate. Wi-Fi is designed for high bandwidth (video, large files) but consumes significant power. Zigbee provides low bandwidth (250 kbps) optimized for small data packets (telemetry, commands) with extremely low power consumption, making it ideal for battery efficiency.
How does Zigbee interference handling work in a busy factory?
Zigbee operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band, sharing space with Wi-Fi. However, it uses 16 separate channels. Implementers typically scan the RF environment and pin the Zigbee network to channels (like 25 or 26) that sit between standard Wi-Fi channels (1, 6, 11) to minimize overlap and packet loss.
What is the effective range of a Zigbee node?
A single point-to-point Zigbee connection typically has a range of 10 to 100 meters depending on line-of-sight and transmit power. However, because of the mesh topology, the effective range of the network is theoretically indefinite, as data hops from robot to robot to cover the entire facility.
Is Zigbee fast enough for real-time robot control?
Zigbee has a latency of roughly 15ms to 30ms per hop. While this is sufficient for supervisory control, issuing target coordinates, and status updates, it is generally not fast enough for real-time "joysticking" or high-frequency closed-loop control, which should be handled by onboard processors.
How many devices can a single Zigbee network support?
The Zigbee addressing scheme supports up to 65,535 nodes on a single network. In practice, due to traffic congestion and coordinator memory limits, industrial networks are typically segmented into clusters of a few hundred nodes to ensure optimal performance and low latency.
What happens if the Coordinator node fails?
In older Zigbee implementations, a Coordinator failure could be catastrophic. Modern Zigbee 3.0 stacks allow for more robust distributed security handling. While new devices cannot join without a Coordinator, existing mesh traffic between Routers (AGVs) continues to function, ensuring operations don't halt immediately.
Can Zigbee penetrate thick warehouse walls?
2.4 GHz signals struggle with thick concrete or metal racking. This is where the mesh shines; instead of trying to penetrate a wall, the signal is routed around obstacles via other nodes. For distinct rooms, it is recommended to place static mains-powered Routers in doorways to bridge areas.
Is the data transmitted over Zigbee secure?
Yes. Zigbee uses AES-128 encryption for securing the network key and the frames. It also employs frame counters to prevent replay attacks. For sensitive industrial applications, install codes are used to ensure only authorized devices can join the mesh.
How does Zigbee compare to LoRaWAN for robotics?
LoRaWAN offers much longer range (kilometers) but very low data rates and high latency, making it suitable for static sensors but poor for robot control. Zigbee offers a balanced middle ground: sufficient speed for telemetry and mesh capabilities for facility-wide coverage.
Can I update robot firmware over Zigbee (OTA)?
Yes, Zigbee supports Over-The-Air (OTA) updates. However, due to the low bandwidth (250 kbps), updating a large firmware file across a fleet can take a significant amount of time and network duty cycle. It is often recommended to use Wi-Fi or physical connections for large updates.
Does Zigbee work with ROS (Robot Operating System)?
Yes, there are several ROS packages (like `zigbee_serial` or bridge nodes for MQTT-to-Zigbee) that allow ROS-based robots to interface with Zigbee modules (like XBee or TI CC2531) via UART or USB, enabling seamless integration into the ROS computation graph.
What hardware is required to add Zigbee to an existing AGV?
Integration is usually simple. Most industrial AGVs add a Zigbee module (e.g., Digi XBee, Silicon Labs) connected via a standard serial interface (UART/SPI) to the main PLC or microcontroller. An antenna mount on the exterior of the chassis is required for optimal signal propagation.
Ready to implement Zigbee in your fleet?
Upgrade your swarm intelligence with robust, low-latency mesh networking.
Explore Our Robots