Wireless Inductive Charging
Revolutionize your AGV and AMR fleets with contactless power transfer. Eliminate mechanical connectors to achieve 24/7 autonomous operation, reduced maintenance costs, and superior safety in challenging environments.

Core Concepts
Electromagnetic Induction
Utilizes magnetic fields to transfer energy between a transmitting coil on the floor and a receiving coil on the robot, eliminating physical contact.
Maintenance Free
With no mechanical brushes or copper contacts to wear out, inductive systems virtually eliminate charger maintenance and contact replacement downtime.
Opportunity Charging
Enables "snack charging" during short pauses in the workflow. High-current bursts keep batteries topped up without long downtimes.
Enhanced Safety
No exposed live contacts means no risk of electric shock or sparks, making it safe for humans and hazardous environments (ATEX).
High Tolerance
Modern systems offer generous misalignment tolerances, allowing AGVs to charge efficiently even if they don't dock with millimeter precision.
Smart Integration
Built-in communication allows the charger and robot BMS to exchange data regarding battery health, charge state, and power regulation.
How It Works
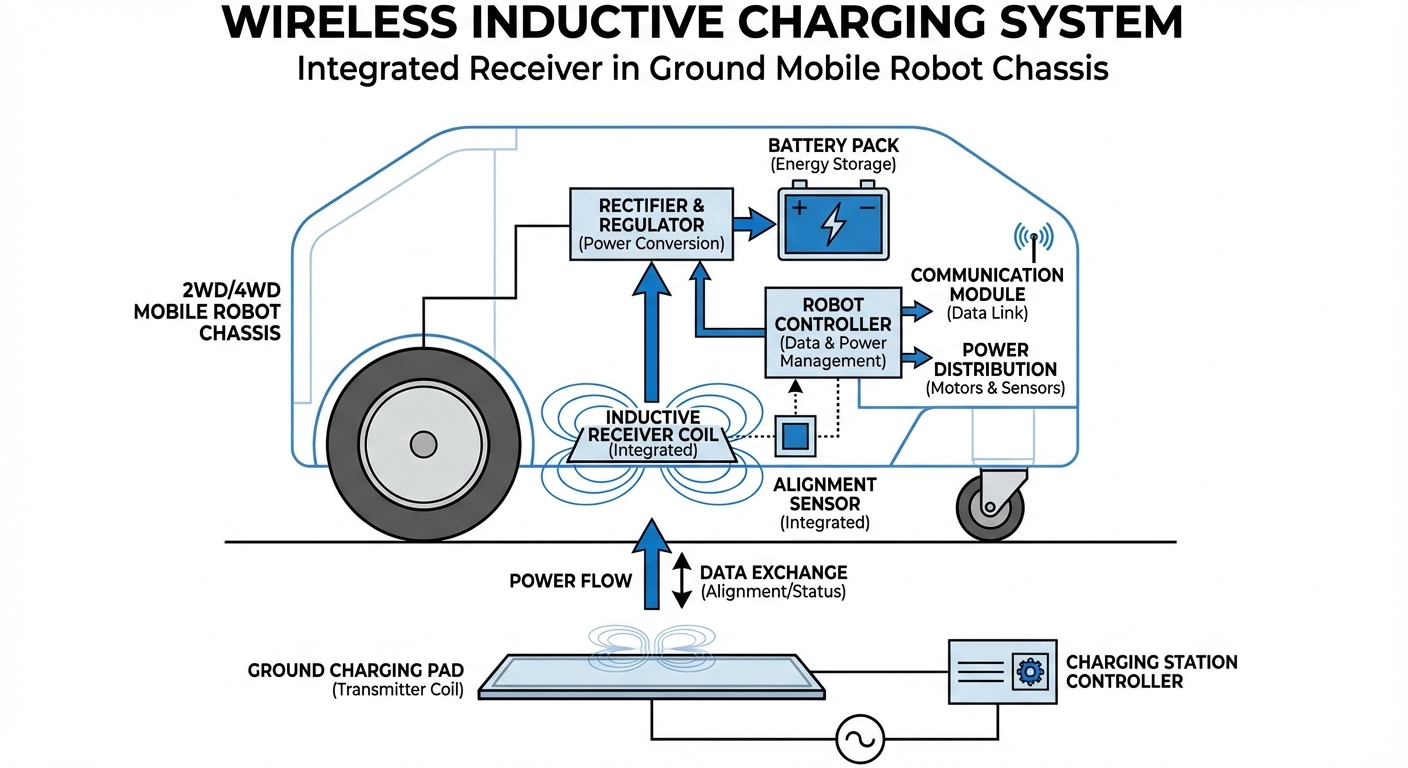
Wireless inductive charging relies on the principle of resonant magnetic coupling. A primary coil (the transmitter), usually embedded in the floor or a charging mat, generates an oscillating magnetic field when powered by the grid.
A secondary coil (the receiver), mounted on the underside or side of the AGV, intercepts this magnetic field. Through magnetic resonance, the energy is captured and converted back into electrical current to charge the onboard battery pack.
Advanced electronics manage the frequency and power delivery to ensure efficiency rates that now rival traditional wired connections (often exceeding 93%), while actively monitoring for Foreign Objects (FOD) to prevent overheating.
This process happens seamlessly the moment the robot positions itself over the pad, requiring no mechanical actuation or manual intervention.
Real-World Applications
Cleanroom Environments
Ideal for semiconductor and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Traditional contact chargers generate copper dust and particulates through friction; inductive charging is completely clean and sealed.
24/7 Logistics Warehouses
Supports "Always-On" logistics. Robots charge for 2-3 minutes at loading stations (Opportunity Charging), eliminating the need to swap batteries or take robots offline for hours.
Hazardous Areas
Essential for oil, gas, and chemical industries. By removing the spark potential of physical connection points, wireless charging enables explosion-proof (ATEX) certified autonomous fleets.
Outdoor Surveillance
Perfect for outdoor security robots exposed to rain, snow, and dirt. Completely sealed electronics (IP67/IP68) function reliably where exposed contacts would corrode or short circuit.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical efficiency of wireless charging compared to wired charging?
Modern resonant inductive charging systems are highly efficient, typically achieving 90% to 94% wall-to-battery efficiency. This is comparable to high-quality wired chargers, meaning there is negligible energy loss penalty for choosing wireless convenience.
How precise does the robot positioning need to be?
Unlike early generation tech, modern systems offer significant tolerance. Most industrial units allow for misalignment of ±30mm to ±50mm in X and Y directions, and several degrees of angular rotation, making docking easy for standard navigation systems.
Is it safe for humans to walk over the charging pads?
Yes. Systems are equipped with Foreign Object Detection (FOD) and Living Object Detection (LOD). If a person or metal object is detected between the coils, the system instantly cuts power to prevent heating or radiation exposure, ensuring compliance with ICNIRP safety guidelines.
What types of batteries are supported?
Wireless charging is agnostic to battery chemistry but is most commonly paired with Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4, NMC) or Supercapacitors. The charging system communicates with the battery's BMS to strictly follow the required CC/CV charging profile.
Can we retrofit existing AGVs with wireless charging?
Yes, retrofitting is a common practice. It involves mounting a receiver plate on the robot and connecting it to the battery terminals and BMS. The footprint is usually compact, allowing installation on existing fleets without major chassis modifications.
What are the power capabilities (charging speed)?
Systems scale from 1kW for small AMRs up to 30kW+ for heavy-duty forklifts and tuggers. High-power systems enable fast "opportunity charging," delivering significant energy in just a few minutes during loading/unloading stops.
Does the charging system require an internet connection?
Basic operation does not require internet; communication happens locally between the pad and robot via the magnetic field or short-range radio. However, for fleet analytics and predictive maintenance, connecting the base station to the local network is recommended.
How does it handle wet or dusty environments?
This is a primary advantage of the technology. Charging pads are typically fully encapsulated (IP67 or IP68 rated). They can function while submerged in water, covered in mud, or coated in heavy dust, conditions that would cause immediate failure for contact chargers.
Will it interfere with Wi-Fi or other robot sensors?
No. Inductive charging operates at low frequencies (typically 20kHz to 140kHz), which is far below the GHz spectrum used by Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and LiDAR. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) shielding ensures no interference with sensitive onboard electronics.
What is the expected lifespan of the hardware?
Since there are no moving parts or physical contacts to wear down, the hardware lifespan is exceptionally long, often exceeding 10-15 years. The electronics usually outlast the service life of the AGV itself.
How does the cost compare to traditional contact charging?
The initial capital expenditure (CapEx) is higher for wireless systems. However, the Operational Expenditure (OpEx) is significantly lower due to zero maintenance, fewer spare parts, and increased vehicle uptime, resulting in a favorable ROI over 2-3 years.
Can multiple robots use the same charger?
Yes. As long as the voltage and power ratings are compatible, a single charging station can serve a mixed fleet of robots. The intelligent communication protocol identifies the robot and adjusts parameters accordingly.
Ready to implement Wireless Inductive Charging in your fleet?
Upgrade your autonomy with robust, maintenance-free power solutions.
Explore Our Robots