Wi-Fi 6 for Robotics
Unlock the next generation of autonomous fleet management with 802.11ax technology. Wi-Fi 6 delivers the deterministic latency, high device density, and power efficiency required for modern AGVs and AMRs to operate safely and seamlessly.

Core Concepts
OFDMA Efficiency
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access allows routers to communicate with multiple robots simultaneously, drastically reducing command latency.
Target Wake Time (TWT)
Robots can "sleep" their radios when data isn't being transmitted, significantly extending battery life for AMRs between charging cycles.
WPA3 Security
Enhanced encryption protocols protect your fleet management system from intrusion, ensuring mission-critical data remains secure.
Seamless Roaming
Improved handover protocols ensure AGVs maintain connection while moving rapidly between access points in large warehouses.
BSS Coloring
Reduces interference in crowded industrial environments by "coloring" data packets, allowing robots to ignore signals from neighboring networks.
High Throughput
Supports the massive bandwidth required for real-time video streaming, LiDAR mapping, and SLAM data processing.
How It Works
Wi-Fi 6 addresses the fundamental challenge of "noisy" industrial environments. Unlike previous generations that used a "listen-before-talk" protocol—which caused delays when many robots operated in the same aisle—Wi-Fi 6 introduces deterministic scheduling.
Through MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) and OFDMA, the network acts like a traffic controller, assigning specific sub-channels to different robots simultaneously. This ensures that a video feed from one robot doesn't block the safety-stop signal of another.
The result is a network that behaves more like a wired connection, providing the reliability required for Level 4 and Level 5 autonomy while maintaining the flexibility of wireless deployment.
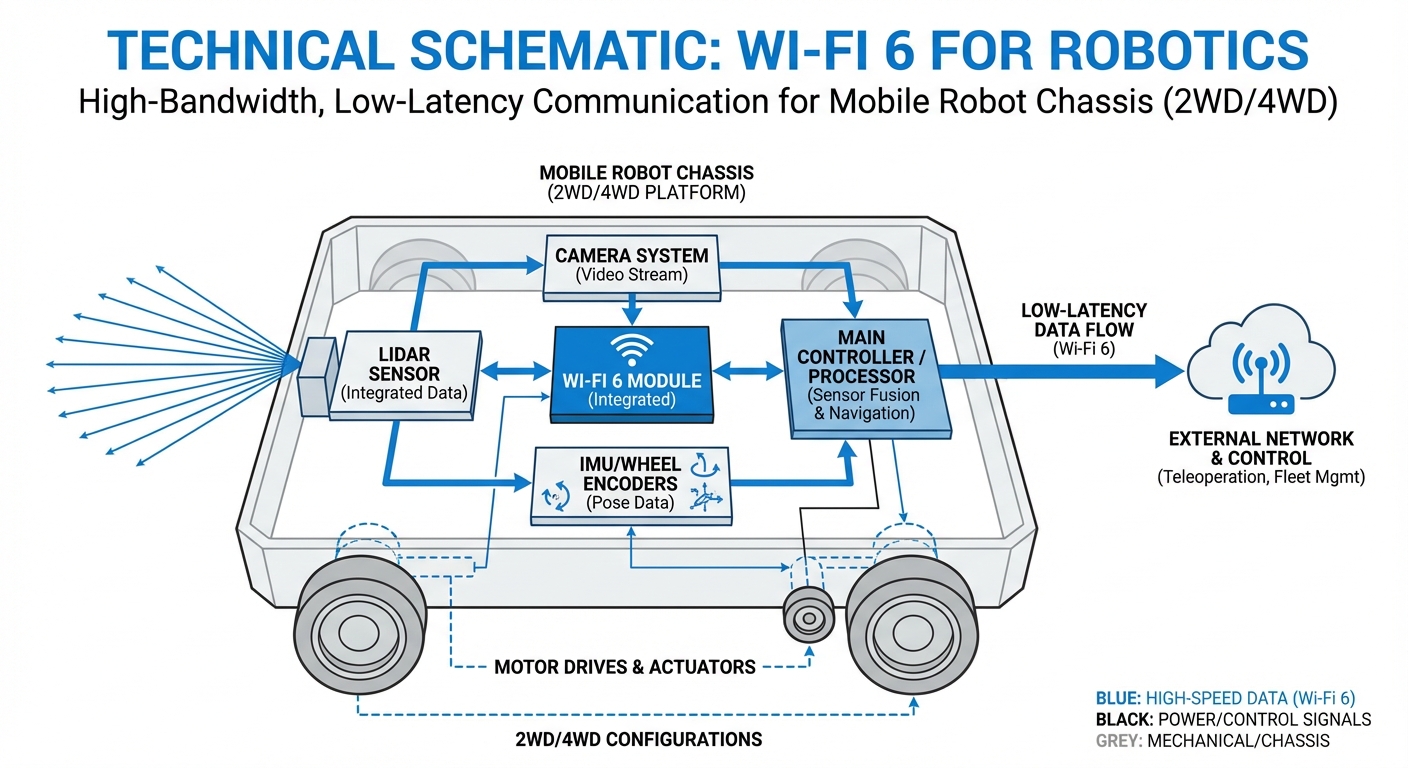
Real-World Applications
High-Density Warehousing
In fulfillment centers with hundreds of AMRs operating in close proximity, Wi-Fi 6 prevents network congestion, ensuring swarm algorithms function without packet loss or collisions.
Automated Manufacturing
Factories full of metal structures and heavy machinery create signal interference. Wi-Fi 6's beamforming and BSS coloring cut through the noise for reliable material transport.
Healthcare Logistics
Service robots in hospitals require strict data privacy and seamless roaming between floors. WPA3 security and fast handover protocols make Wi-Fi 6 ideal for sensitive environments.
Hazardous Environments
For teleoperated robots in nuclear or chemical plants, low latency is a safety requirement. Wi-Fi 6 provides near real-time feedback for remote operators controlling delicate manipulators.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes Wi-Fi 6 better than Wi-Fi 5 for robots?
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) introduces OFDMA, which splits channels into smaller sub-channels. This allows the router to communicate with multiple robots simultaneously rather than sequentially, reducing latency by up to 75% in crowded environments compared to Wi-Fi 5.
Should I choose Wi-Fi 6 or private 5G for my AGV fleet?
It depends on the environment. Wi-Fi 6 is generally more cost-effective and easier to deploy for indoor environments like warehouses. Private 5G excels in outdoor, wide-area coverage or extremely mobile scenarios, but often comes with higher infrastructure costs.
How does Wi-Fi 6 improve robot battery life?
Through a feature called Target Wake Time (TWT). The router schedules specific times for the robot to wake up and exchange data. This allows the Wi-Fi radio to sleep for longer periods, reducing power consumption significantly compared to constant polling.
Can I retrofit my existing robots with Wi-Fi 6?
Yes, most industrial PCs and robot controllers can be upgraded via M.2 Wi-Fi 6 modules or external industrial Wi-Fi 6 bridges connected via Ethernet. However, both the robot client and the access points must support Wi-Fi 6 to see benefits.
What is the typical range of a Wi-Fi 6 access point in a warehouse?
While range is similar to Wi-Fi 5 (roughly 30-50 meters indoors depending on obstructions), Wi-Fi 6 handles weak signals better at the edge of coverage. However, 2.4GHz signals travel further than 5GHz or 6GHz, so band planning is crucial for large facilities.
Does Wi-Fi 6 solve interference from metal racking?
It helps but doesn't eliminate physics. Wi-Fi 6 uses better beamforming to direct signals toward the robot rather than radiating everywhere, and BSS Coloring helps ignore signals from neighboring networks, but proper AP placement is still required around metal obstructions.
Is WPA3 mandatory for Wi-Fi 6 robotics?
While Wi-Fi 6 devices are required to support WPA3 for certification, they can often fall back to WPA2. However, for industrial robotics, WPA3 is highly recommended due to its protection against offline dictionary attacks and better encryption for sensitive data.
How does Wi-Fi 6 handle video streaming from robots?
Excellently. The higher throughput (up to 9.6 Gbps theoretical) and OFDMA allow for consistent uplink performance. This is critical for teleoperation or AI-based vision systems that need to offload processing to a central server without video lag.
Does Wi-Fi 6E (6GHz) offer advantages over standard Wi-Fi 6?
Yes, Wi-Fi 6E adds the 6GHz band, which offers wider channels and no interference from legacy devices (like microwaves or old Wi-Fi). It is ideal for ultra-low latency, though the range is shorter than 5GHz and requires Line of Sight.
What happens if a robot roams between Access Points?
Wi-Fi 6 utilizes standards like 802.11r/k/v for fast roaming. When properly configured, a robot can switch APs in under 50ms, which is fast enough to maintain a persistent connection to the Fleet Management System without triggering a safety stop.
How many robots can one Wi-Fi 6 AP handle?
While theoretical limits are high, practical industrial deployments typically see 30-50 active clients per radio without performance degradation. This is a significant improvement over Wi-Fi 5, which often struggled with 15-20 active high-bandwidth clients.
Is latency deterministic in Wi-Fi 6?
It is much closer to deterministic than previous generations due to scheduled resource units (OFDMA). While not as strictly deterministic as a wired TSN (Time Sensitive Network), it is sufficient for most soft-real-time industrial control loops.