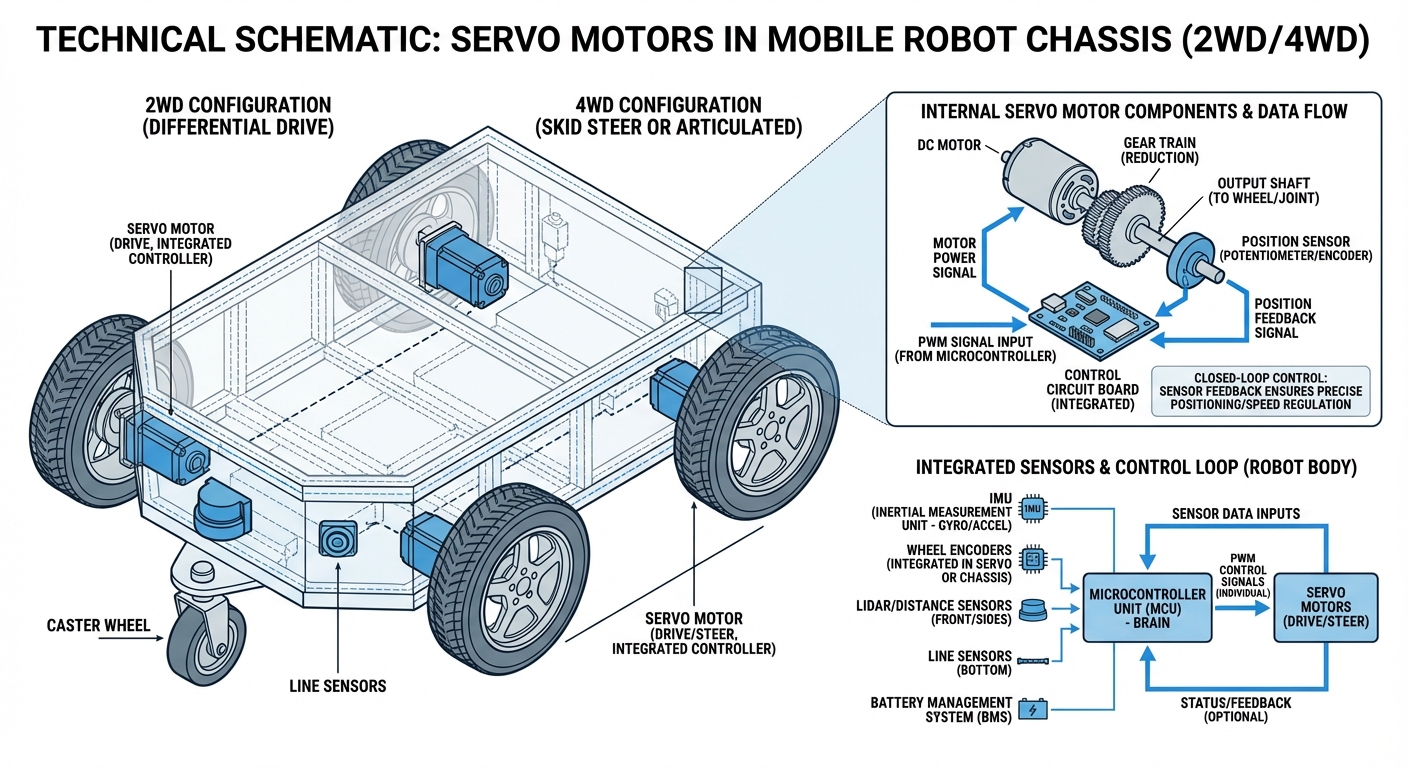
Servo Motors
Servo motors are the precision actuators behind modern Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs), converting electrical signals into exact mechanical position, speed, and torque. By utilizing closed-loop feedback systems, they enable robots to navigate complex environments with millimeter-level accuracy.

Core Concepts
Closed-Loop Control
Unlike stepper motors, servos operate on a feedback loop. They constantly verify their actual position against the target position and self-correct instantly.
Feedback Encoders
Integrated sensors (encoders) track the rotation of the motor shaft. This data is critical for odometry calculations in AGV navigation and localization.
High Torque Density
Servo motors provide high torque relative to their size, even at high speeds. This allows compact AGVs to carry heavy payloads without stalling.
PID Control
The controller uses Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) algorithms to smooth out movements, preventing jerky acceleration or overshoot during stops.
Dynamic Response
Servos offer rapid acceleration and deceleration. This agility allows mobile robots to react quickly to obstacles or changes in path planning.
Efficiency
They draw current proportional to the mechanical load. When an AGV is idle or carrying a light load, power consumption drops, extending battery life.
How It Works
At the heart of a servo system is the relationship between the controller, the motor, and the feedback device. In an AGV application, the main computer sends a command signal (usually via CANopen or EtherCAT) specifying the desired position or velocity.
The servo drive amplifies this signal to power the motor. As the motor turns, the encoder sends real-time data back to the drive. The drive compares the actual position with the target position hundreds of times per second.
If there is a discrepancy (error), the drive adjusts the voltage and current supplied to the motor to correct it. This continuous loop ensures that if an AGV hits a bump or carries a heavier load, the wheels maintain the correct speed and trajectory.
Real-World Applications
Drive & Steering
Servos power the main drive wheels in differential drive AGVs and govern the steering angle in Ackerman-steering AMRs, ensuring precise path following in narrow warehouse aisles.
Heavy Lifting
In automated forklift AGVs, high-torque servo motors drive the hydraulic pumps or ball screws required to lift pallets weighing over 1,000kg with smooth vertical motion.
Mobile Manipulation
For AMRs equipped with robotic arms (cobots), mini-servo motors actuate the arm joints, allowing the robot to pick and place individual items from shelves.
Turret & Conveyors
Top-module attachments, such as rotating turrets or roller conveyors, use servos to synchronize speed with factory production lines for seamless material transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a Servo Motor and a Stepper Motor?
The primary difference is the feedback loop. Servos use encoders to verify position (closed-loop), providing higher torque at high speeds and better efficiency. Steppers are open-loop and can lose steps if overloaded, making servos superior for dynamic AGV applications.
Why are Brushless DC (BLDC) servos preferred for robotics?
BLDC servos eliminate the mechanical wear of brushes, resulting in a longer lifespan and less maintenance. They also offer a better power-to-weight ratio and generate less heat, which is crucial for battery-operated mobile robots.
What is an Absolute Encoder vs. an Incremental Encoder?
Incremental encoders track motion relative to a starting point and require homing after power loss. Absolute encoders know their exact position immediately upon startup, which is safer and more efficient for autonomous vehicles.
How does PID tuning affect AGV performance?
PID tuning adjusts how the motor responds to error. Poor tuning causes oscillation (shaking) or sluggish response. Proper tuning ensures the AGV accelerates smoothly, stops precisely at docking stations, and maintains straight lines.
Do servo motors consume power when the AGV is stopped?
Yes, but minimal. They may draw a small amount of current to maintain "holding torque" to keep the position against gravity (if on a slope) or external forces. Electronic brakes are often used to cut power completely during long stops.
What is the "Gear Ratio" and why does it matter?
Servo motors often spin too fast for direct wheel drive. A gearbox reduces speed and multiplies torque. Choosing the right ratio balances maximum speed against the ability to carry heavy loads or climb ramps.
How do communication protocols like CANopen apply here?
Protocols like CANopen or EtherCAT allow the robot controller to communicate with multiple servo drives simultaneously over a single cable. They enable real-time synchronization of wheels for complex maneuvers like rotation in place.
What causes servo motor overheating?
Overheating usually results from undersizing the motor for the load, aggressive duty cycles (constant acceleration/deceleration), or friction in the drivetrain. Thermal sensors usually trigger a shutdown to prevent damage.
Are servo motors waterproof?
Standard servos are not. For AGVs operating in outdoor or wash-down environments (like food processing), specific IP65 or IP67 rated motors with sealed housings and connectors are required.
Can I mix different brands of motors and drives?
It is possible but complex. It requires matching voltage, current, feedback types, and pinouts perfectly. It is generally recommended to use matched sets or drives with universal compatibility to reduce integration time.
What is "Safe Torque Off" (STO)?
STO is a safety function that prevents the drive from generating torque in the motor. In an emergency stop situation on an AGV, STO ensures the motor cannot unintentionally start, protecting human operators.
Ready to implement Servo Motors in your fleet?
Discover our range of AGV-ready servo solutions designed for industrial reliability.
Explore Our Robots