Mecanum Wheels
Unlock true omnidirectional mobility for AGVs and mobile robots. Mecanum technology allows vehicles to move instantaneously in any direction—sideways, diagonally, or rotating—without changing their heading, revolutionizing navigation in tight spaces.

Core Concepts
Holonomic Motion
Unlike differential drive systems, Mecanum wheels provide 3 degrees of freedom on a plane: X, Y, and Theta (rotation) simultaneously.
45° Roller Geometry
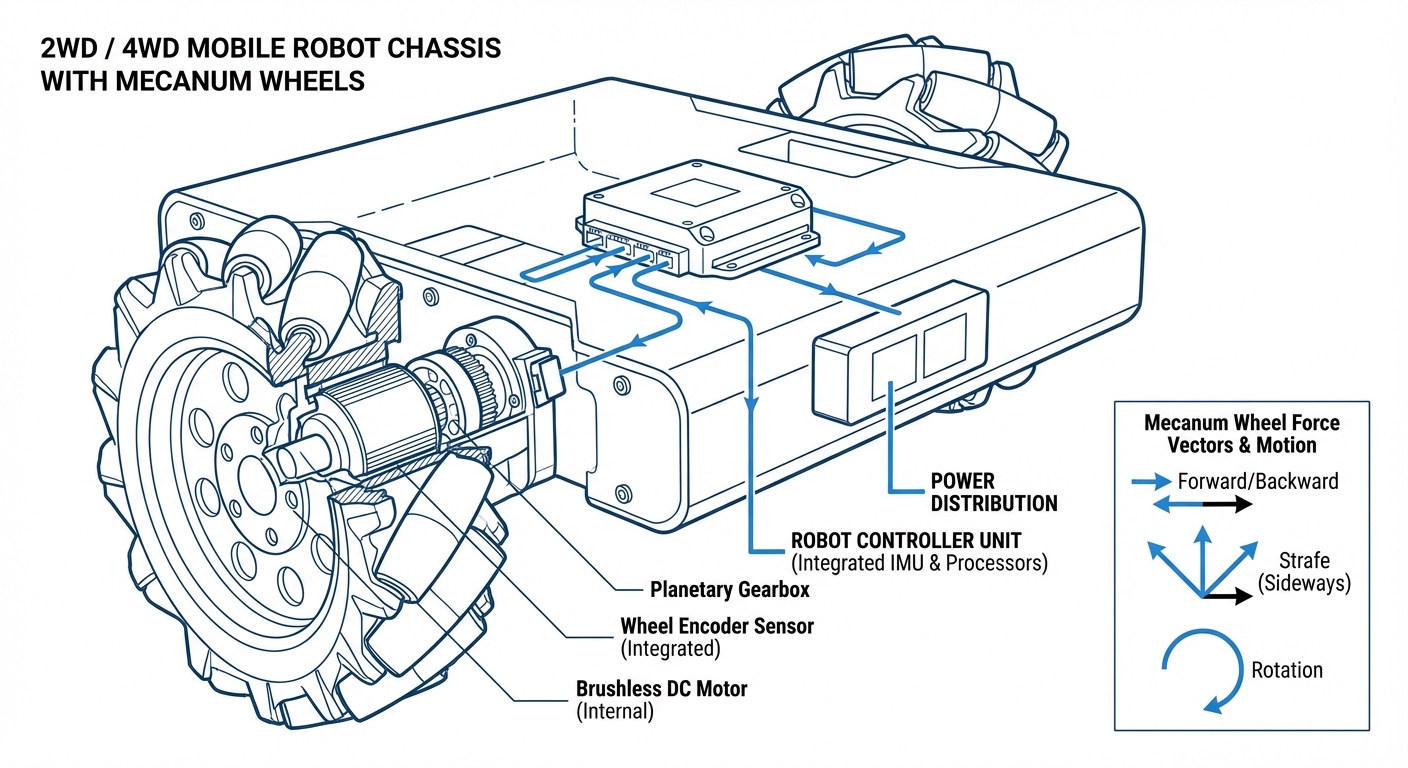
The secret lies in passive rollers attached to the wheel circumference at a 45-degree angle to the wheel's axis of rotation.
Vector Summation
Movement is achieved by vector addition. By spinning wheels in opposing directions, force vectors cancel out to produce sideways strafing.
Zero Turn Radius
The robot can rotate in place perfectly by spinning left wheels in reverse and right wheels forward, requiring zero clearance for turns.
Independent Drive
Each wheel requires its own dedicated motor and gearbox. Mechanical linking is not possible; control is entirely software-driven.
Floor Requirements
Due to small contact points on rollers, Mecanum wheels operate best on hard, flat, and level concrete or industrial flooring.
How It Works: The Physics of Strafing
The magic of the Mecanum wheel lies in the orientation of the forces. When a standard wheel rotates, it generates force only in the forward/backward direction. A Mecanum wheel, however, generates force at a 45-degree angle relative to the chassis because of its free-spinning diagonal rollers.
By mounting four wheels in a specific configuration (often called "X" configuration where rollers point to the center), the control system can sum these force vectors.
For example, to move purely sideways (strafe right): The front-left and back-right wheels spin forward, while the front-right and back-left wheels spin backward. The forward/backward force components cancel each other out, leaving only the sideways force components.
This capability eliminates the need for complex steering linkages (like Ackermann steering) but requires sophisticated kinematic software to calculate wheel speeds instantaneously.
Real-World Applications
Warehouse Logistics
AGVs utilizing Mecanum wheels maximize storage density by navigating extremely narrow aisles. They can pick up pallets and slide sideways out of lanes without needing space to perform a turning radius.
Precise Assembly
In automotive and aerospace manufacturing, large parts must be aligned with millimeter precision. Mecanum platforms allow heavy components to be nudged laterally for perfect bolt-hole alignment.
Maintenance Platforms
Mobile scissor lifts used for aircraft maintenance use omnidirectional wheels to maneuver under fuselages and wings, approaching work areas from any angle without dangerous multi-point turns.
Inspection Robots
Small rovers deployed in cramped environments, such as under-floor cabling ducts or machinery crawl spaces, rely on strafing capabilities to inspect areas standard robots cannot reach.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Mecanum wheels and Omni wheels?
While both provide multidirectional movement, Omni wheels have rollers at 90 degrees to the wheel axis, whereas Mecanum rollers are at 45 degrees. Mecanum wheels allow for a standard chassis configuration (wheels parallel to the robot), whereas Omni wheels often require mounting at angles (like a triangular setup) to achieve holonomic motion.
Can Mecanum wheels operate on carpet or uneven terrain?
Generally, no. Mecanum wheels perform poorly on soft surfaces like thick carpet or rough terrain like gravel. The rollers need a hard surface to slide against to generate the necessary vector forces. On soft surfaces, the rollers sink, increasing friction and preventing the slide required for lateral movement.
Do I need a specific motor configuration?
Yes, you absolutely need four independent motors, one for each wheel. You cannot link the wheels mechanically (e.g., via a single axle for the front pair) because strafing and rotation require the wheels on the same axle to often spin in opposite directions.
Does the orientation of the wheels matter during assembly?
Crucially, yes. Mecanum wheels are handed (left and right versions). They must be installed in an "X" pattern when viewed from above (rollers pointing toward the center). If installed in an "O" pattern, the robot will struggle to rotate and vectoring will be inefficient.
Are Mecanum wheels less efficient than standard wheels?
Yes, typically around 65-70% efficiency compared to standard wheels. Force is lost because the rollers are pushing diagonally against the ground to create forward motion. This results in higher battery consumption for the same distance traveled compared to a skid-steer or differential drive robot.
What is the payload capacity?
Payload capacity is generally lower than standard wheels of the same diameter because the weight is concentrated on the small contact patch of a single roller at any given moment. However, heavy-duty industrial Mecanum wheels exist that can handle thousands of kilograms using high-strength steel rollers.
How does suspension work with Mecanum wheels?
Suspension is difficult but necessary. Ideally, all four wheels must maintain contact with the ground at all times for the vector math to work. If one wheel lifts off due to uneven floor, the robot's movement becomes unpredictable. Often, a "rocker bogie" or independent spring suspension is used.
Why are they noisier than regular wheels?
The noise creates a distinct "clack-clack" sound as the load transfers from one roller to the next. This vibration can be dampened with softer roller materials (like polyurethane), but Mecanum wheels will almost always be louder than pneumatic or solid rubber tires.
Can Mecanum robots climb ramps?
They can climb shallow ramps, but traction is a major issue. Because the rollers are free-spinning, gravity can cause the robot to slide sideways or backwards if the incline is too steep. They are generally not recommended for inclines greater than 5-10 degrees.
What kind of sensors are needed for navigation?
High-resolution rotary encoders on each motor are mandatory to ensure wheels spin at the precise speeds required by the kinematic model. For external navigation (SLAM), LIDAR and IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units) are critical to correct for the slight slipping inherent in Mecanum movement.
Are there maintenance concerns?
Yes. The small axles of the rollers can gather hair, dust, and debris from a warehouse floor, causing rollers to seize. If a roller seizes, the wheel acts like a standard wheel, breaking the strafing physics. Regular cleaning and lubrication are required.
How fast can they go?
Speed is generally comparable to standard wheels, limited mostly by motor RPM and gearbox ratios. However, at high speeds, the vibration from roller transition increases significantly, which can affect sensor readings and structural integrity.