LoRaWAN
Unlock massive-scale fleet connectivity with the Low Power Wide Area Network protocol. Designed for the industrial edge, LoRaWAN enables AGVs to transmit critical telemetry over kilometers while penetrating dense warehouse infrastructure, all with minimal energy footprint.

Core Concepts
Long Range Coverage
Capable of transmitting signals up to 15km in rural areas and deep into complex indoor environments, eliminating dead zones common with Wi-Fi.
Ultra-Low Power
Optimized for small data packets, allowing battery-operated IoT sensors and robot modules to run for years without recharging.
Deep Indoor Penetration
Uses sub-gigahertz radio waves (CSS modulation) to easily pass through concrete walls, metal racking, and multiple floors.
Star Topology
Devices communicate directly with gateways rather than meshing. This simplifies the network and reduces battery drain caused by relaying messages.
AES-128 Security
End-to-end encryption ensures that telemetry data regarding fleet location and status remains secure from the edge to the application server.
Adaptive Data Rate
The network automatically optimizes data rates, airtime, and energy consumption for each specific end-node based on signal quality.
How It Works: Chirp Spread Spectrum
LoRaWAN operates on a physical layer technology called LoRa, which uses Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) modulation. Unlike standard amplitude or frequency modulation, CSS encodes data into "chirps"—sweeping signals that are incredibly resilient to interference and noise.
In a robotic context, the AGV acts as an "End Node." It broadcasts small packets of telemetry (battery status, X/Y coordinates, error codes) asynchronously. These signals are picked up by one or more Gateways, which act as transparent bridges relaying messages to a central Network Server via standard IP connections (Ethernet/Cellular).
The Network Server handles deduplication (if multiple gateways hear the robot), security decryption, and adaptive rate control, before pushing the clean JSON data to your Fleet Management System. This architecture allows thousands of robots to communicate with just a handful of gateways.
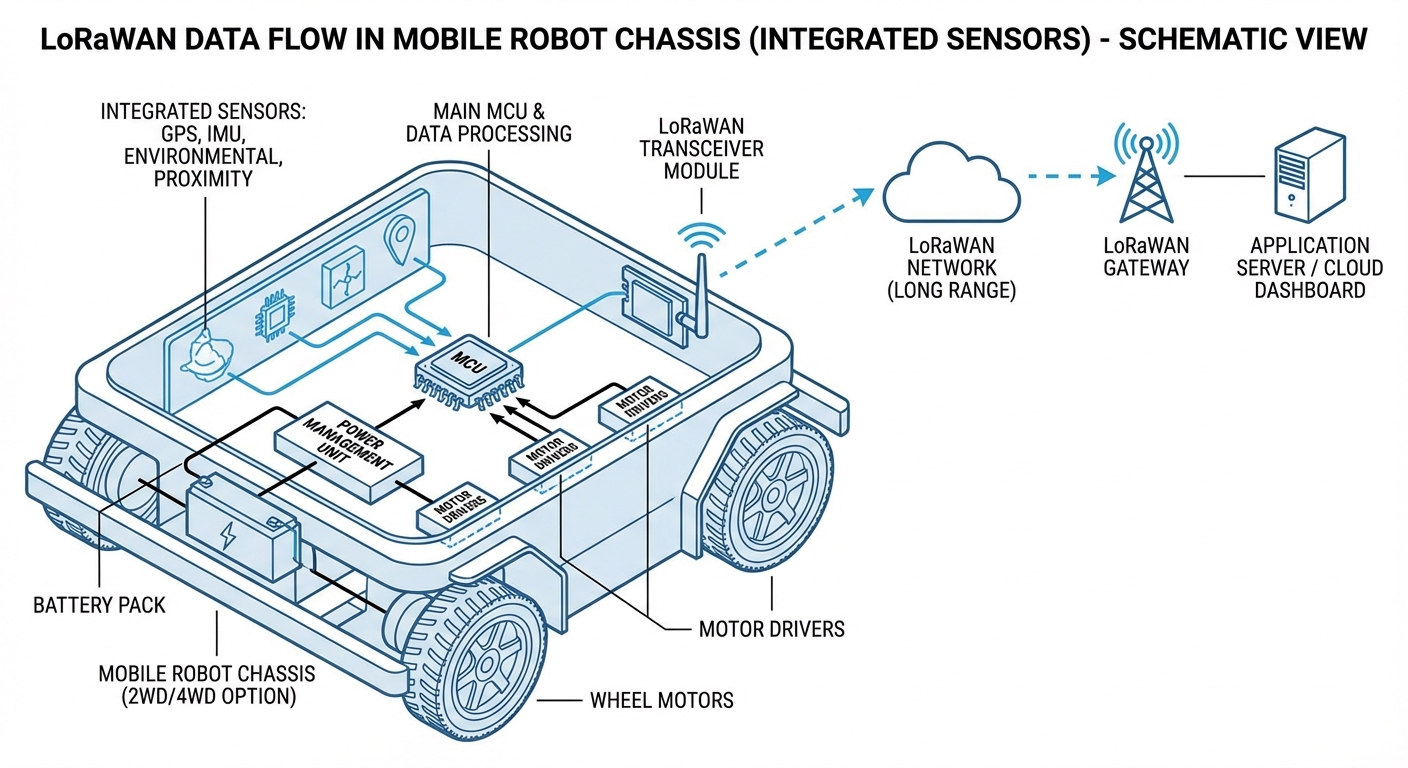
Real-World Applications
Mega-Warehouse Asset Tracking
In 500,000+ sq ft facilities where Wi-Fi coverage is spotty or expensive to maintain, LoRaWAN provides reliable, low-bandwidth location updates for pallet jacks and forklifts.
Outdoor Agriculture Robotics
For autonomous tractors or harvesters operating in vast fields without cellular coverage, LoRaWAN offers a private network solution for sending "heartbeat" status signals.
Predictive Maintenance
Robots equipped with vibration and temperature sensors can send periodic health reports via LoRaWAN, independent of the main control network, ensuring maintenance alerts are never missed.
Mining & Underground Operations
Due to its superior penetration capabilities, LoRaWAN is ideal for tracking AGVs in mines or tunnels where high-frequency signals like 2.4GHz or 5GHz fail to propagate.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can LoRaWAN replace Wi-Fi for controlling AGVs?
No, LoRaWAN is not suitable for real-time control (teleoperation). Its latency (seconds) and low bandwidth (bytes per second) make it impossible to stream video or send instant motor commands. It is best used for non-critical telemetry, asset tracking, and status monitoring alongside a high-speed local network.
What is the typical range in an industrial warehouse?
While outdoor range can exceed 10km, indoor industrial range typically falls between 2km to 3km. However, this is significantly better than Wi-Fi; a single LoRaWAN gateway can often cover an entire large logistics center, penetrating metal racking and concrete walls that would block higher frequencies.
How does LoRaWAN handle network congestion with many robots?
LoRaWAN gateways are multichannel and can process messages on different frequency channels and spreading factors simultaneously. However, due to duty-cycle regulations, it is critical to limit how often each robot transmits. It is designed for periodic updates (e.g., every minute), not continuous streaming.
Is the data transmission secure?
Yes, LoRaWAN implements two layers of AES-128 encryption: Network Session Keys (verifying the node's authenticity) and Application Session Keys (encrypting the payload). The gateway cannot read the payload data; only the application server possessing the keys can decrypt the telemetry.
What is the difference between Public and Private LoRaWAN?
A Public network (like The Things Network or Helium) uses shared infrastructure where you pay for connectivity or use community gateways. A Private network involves installing your own gateways and Network Server (e.g., ChirpStack) on-premise, giving you full control over latency, coverage, and data sovereignty, which is preferred for industrial robotics.
Does LoRaWAN interfere with factory Wi-Fi or Bluetooth?
Generally, no. LoRaWAN operates in the sub-gigahertz ISM bands (868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in US). Wi-Fi and Bluetooth operate at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Because they operate on vastly different frequencies, they coexist without causing interference to one another.
Can I use LoRaWAN for indoor geolocation?
Yes, using a technique called TDoA (Time Difference of Arrival). If a robot's signal is received by three or more gateways, the network can triangulate its position. However, the accuracy is coarse (20-100 meters) compared to LiDAR or UWB, making it suitable for "zone" tracking rather than precise navigation.
What is the maximum payload size?
Payload size varies by Spreading Factor (range). It typically ranges from 51 bytes to 222 bytes. This limitation enforces efficient data encoding; developers usually send binary or hex data rather than verbose JSON strings to maximize efficiency.
What happens if a gateway goes offline?
LoRaWAN networks are resilient. If you have overlapping coverage (multiple gateways), the robot's message will simply be picked up by the next available gateway. The robot does not bond to a specific gateway; it broadcasts to the network as a whole.
How much power does a LoRaWAN module consume?
Consumption is extremely low. In sleep mode, a module draws micro-amps. During transmission, it might draw 30-40mA for a few milliseconds. For an AGV with a massive battery, this is negligible, but for battery-powered external sensors, it enables 5-10 year lifespans.
Is it expensive to implement?
Compared to a mesh Wi-Fi network requiring cabling and APs every 50 meters, LoRaWAN is very cost-effective. A single industrial gateway costs a few hundred dollars and covers kilometers. The end-node modules for the robots are also inexpensive commodity hardware.
Ready to implement LoRaWAN in your fleet?
Scale your operations with connectivity that reaches further.
Explore Our Robots