Lithium-Ion Batteries
Revolutionizing autonomous logistics with high energy density and rapid opportunity charging. Lithium-Ion technology eliminates downtime, providing the consistent, clean power required for 24/7 mobile robot operations.

Core Concepts
Energy Density
Lithium-ion cells pack significantly more energy into a smaller footprint compared to lead-acid alternatives. This allows compact AGVs to carry heavier payloads without sacrificing internal space.
Opportunity Charging
Unlike older battery chemistries, Li-Ion supports rapid charging during short breaks. A robot can gain substantial runtime from a 10-minute charge, enabling continuous 24-hour workflows.
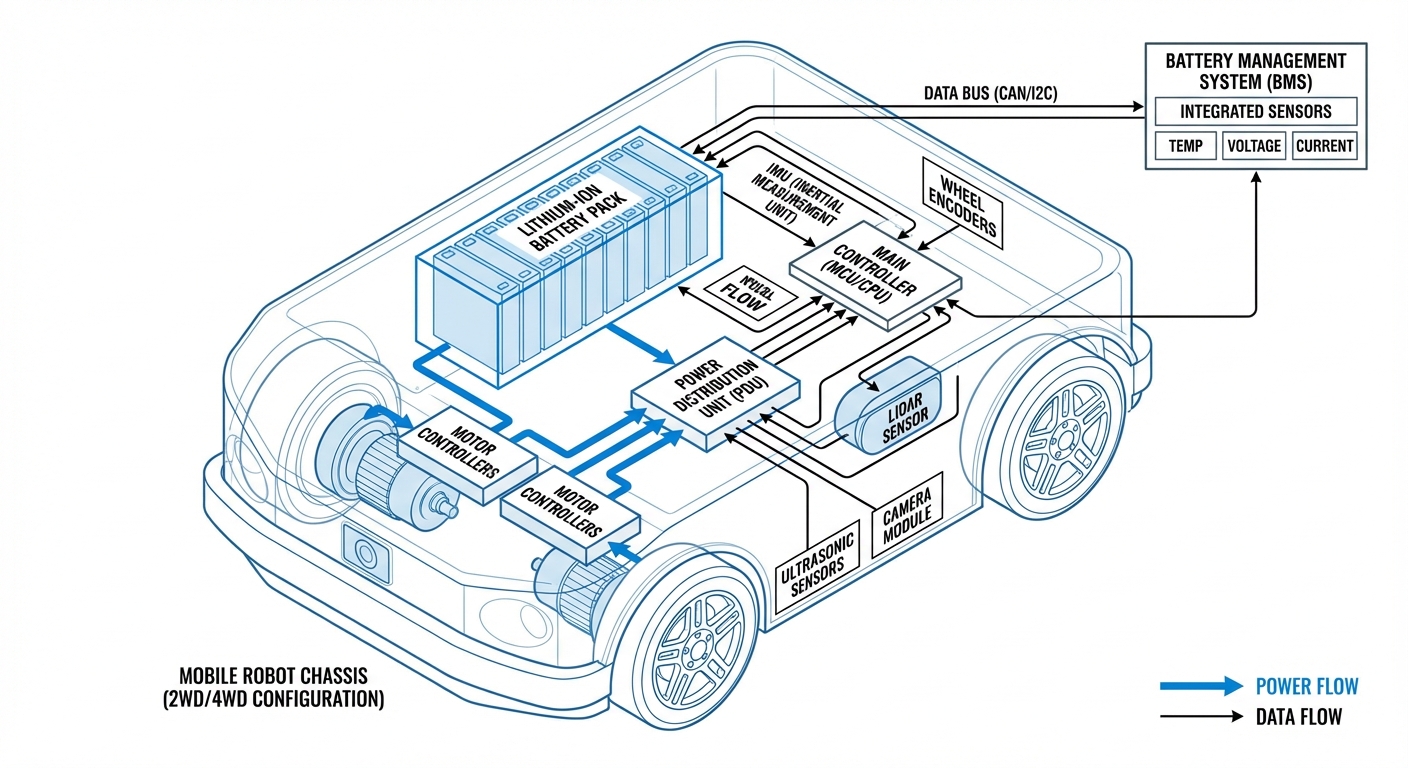
BMS Integration
The Battery Management System (BMS) is the brain of the pack. It communicates directly with the robot's controller via CAN bus to monitor cell voltage, temperature, and prevent over-discharge.
Cycle Life
Li-Ion batteries typically offer 3,000 to 5,000 charge cycles before capacity degrades significantly. This longevity results in a lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the robot's lifetime.
Maintenance Free
These batteries are sealed and require no watering or active maintenance. This is crucial for autonomous fleets where human intervention for maintenance defeats the purpose of automation.
Consistent Voltage
Li-Ion maintains a stable voltage curve throughout the discharge cycle. This ensures that AGV motors perform with consistent torque and speed regardless of whether the battery is at 90% or 20% charge.
How It Works: The Chemistry of Autonomy
At the heart of every Lithium-Ion battery pack used in robotics is the movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode during charge and discharge cycles. In a robotics context, individual cells (typically cylindrical 18650/21700 or prismatic format) are wired in series and parallel configurations to achieve the specific voltage (usually 24V or 48V) and capacity required for the AGV.
Unlike consumer electronics, industrial robotics batteries are equipped with a sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS). The BMS acts as a gatekeeper, balancing the charge across cells to ensure uniformity. If one cell degrades or overheats, the BMS isolates the issue and communicates a warning to the robot's central processing unit to initiate a safety stop or return to a charging station.
The high discharge rate capabilities of Lithium chemistry allow robots to handle spikes in power demand, such as lifting heavy pallets or accelerating ramps, without voltage sag that could cause system resets.
Real-World Applications
E-Commerce Warehousing
In massive fulfillment centers, AMR fleets operate 24/7 using opportunity charging. Li-Ion batteries allow robots to dock for 5 minutes every hour, eliminating the need for battery swapping rooms and maximizing fleet utilization.
Cleanroom Manufacturing
Semiconductor and pharmaceutical manufacturing require zero emissions. Unlike lead-acid batteries which can off-gas hydrogen, sealed Li-Ion packs are perfectly safe for ISO-certified cleanroom environments.
Heavy Payload Transport
For automotive assembly AGVs moving chassis weighing tons, the high energy density of Li-Ion provides the necessary kilowatt-hours to drive powerful traction motors without adding excessive weight to the vehicle itself.
Cold Chain Logistics
Modern Li-Ion packs with integrated heating elements perform exceptionally well in refrigerated warehouses. They maintain efficiency in sub-zero temperatures where other battery chemistries suffer severe capacity loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary advantage of Li-Ion over Lead-Acid for AGVs?
The primary advantage is "opportunity charging" combined with zero maintenance. Li-Ion batteries can accept high current for short periods without damage, allowing robots to charge during brief pauses in workflow, whereas lead-acid requires long, uninterrupted charge cycles and regular water maintenance.
How does the Battery Management System (BMS) ensure safety?
The BMS continuously monitors the voltage, current, and temperature of every cell in the pack. If it detects conditions that could lead to thermal runaway or damage (like over-voltage or extreme heat), it electronically disconnects the battery from the load and sends an error code to the robot controller.
What is the expected lifespan of a Li-Ion battery in a robotics application?
In typical industrial applications, a Li-Ion battery can last between 3,000 to 5,000 full charge cycles while retaining at least 80% of its original capacity. For a robot running 24/7, this often translates to 5 to 7 years of service life before replacement is needed.
Can I retrofit an existing lead-acid AGV with Lithium-Ion batteries?
Yes, retrofitting is common, but it requires checking the counterweight balance since Li-Ion is lighter. Additionally, the charger must be replaced or reprogrammed for a Lithium charging profile, and the battery gauge may need updating to accurately read the state of charge (SoC).
Does Li-Ion technology present a fire risk in warehouses?
While Li-Ion chemistry has a higher energy density, modern industrial packs use LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) chemistry which is extremely stable and resistant to thermal runaway. Combined with redundant BMS safety protections, the risk is minimal and comparable to other industrial equipment.
How does temperature affect Li-Ion performance?
Li-Ion batteries perform best between 10°C and 30°C. Charging is generally restricted below freezing (0°C) to prevent lithium plating, which damages cells; however, discharge is possible at lower temperatures, and many packs include internal heaters for cold storage applications.
What is the Depth of Discharge (DoD) recommended for these batteries?
Li-Ion batteries can safely be discharged up to 90-95% (high DoD) without significant damage, giving you access to almost the full rated capacity. In contrast, lead-acid batteries should typically not be discharged below 50% to avoid drastically shortening their lifespan.
How is the State of Charge (SoC) calculated?
The BMS uses "Coulomb Counting" (measuring current in vs. current out) combined with voltage mapping to determine SoC. This data is transmitted via CAN bus to the robot's navigation stack, allowing the fleet manager to autonomously route the robot to a charger when power is low.
Are there recycling options for industrial Li-Ion batteries?
Yes, the industry is rapidly maturing its recycling capabilities. Valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel can be recovered. Many manufacturers now offer end-of-life take-back programs to ensure environmentally responsible disposal and material recovery.
Is the upfront cost higher than traditional batteries?
Yes, the initial purchase price is higher, typically 2-3x that of lead-acid. However, when factoring in the 3x longer lifespan, zero maintenance labor, electricity efficiency, and increased robot uptime, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is significantly lower over 5 years.
Do Li-Ion batteries suffer from "Memory Effect"?
No, Lithium-Ion batteries do not have a memory effect. You do not need to fully discharge them before recharging. In fact, shallow discharges and frequent "top-up" charging (opportunity charging) are preferred and healthy for the battery chemistry.