Cycloidal Gears
Unlock precision motion with the distinct mechanics of cycloidal drives. Designed for high-torque, zero-backlash performance, these gears are the industry standard for next-generation AGVs and mobile robotic actuators.

Core Concepts
Zero Backlash
Unlike standard gears, cycloidal drives maintain continuous contact points, virtually eliminating play. This ensures sub-arcminute positioning accuracy essential for LIDAR navigation.
High Torque Density
Cycloidal gears distribute load across approximately 30% of their teeth simultaneously. This allows compact AGV wheel hubs to move massive payloads without failure.
Shock Load Resistance
Rated to withstand emergency stop forces up to 500% of nominal torque. The internal pins absorb shear stress, preventing catastrophic tooth breakage common in planetary gears.
Rolling Contact
Motion is achieved through rolling rather than sliding friction. This significantly reduces heat generation during continuous AGV operation and extends the component's lifespan.
Compact Footprint
Achieve high reduction ratios (up to 185:1) in a single stage. This allows for flatter robot designs (low profile) ideal for sliding under pallets or warehouse racks.
High Stiffness
The internal rigidity ensures that when the motor stops, the load stops immediately. There is minimal elastic deformation, ensuring high repeatability in pick-and-place tasks.
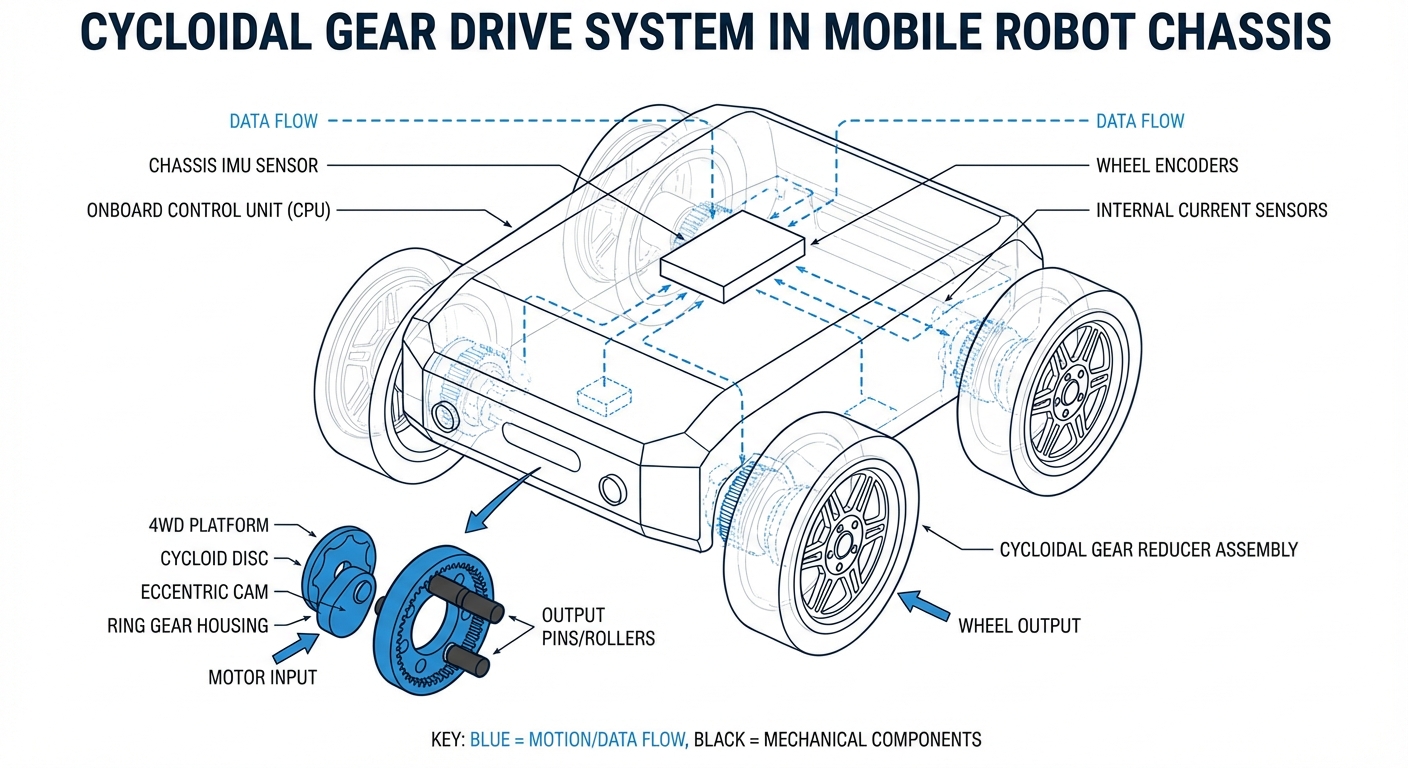
How It Works: The Eccentric Motion
The magic of the cycloidal gear lies in its "wobbling" mechanism. An input shaft drives an eccentric bearing, which causes a cycloidal disc to gyrate inside a housing lined with stationary ring pins.
The disc has N lobes, while the housing has N+1 pins. For every full rotation of the eccentric input shaft, the cycloidal disc is advanced by exactly one tooth pitch in the opposite direction.
This unique reduction mechanism creates a massive gear reduction in a minimal space while maintaining continuous contact between the lobes and pins. The result is smooth, vibration-free transmission of power ideal for sensitive robotic instrumentation.
Real-World Applications
Direct Drive Wheels
Integrated directly into the wheel hub of warehouse AGVs, providing enough torque to move 1,000kg+ loads from a standstill without external belts or chains.
Robotic Articulation
Used in the joints of mobile manipulators (robotic arms mounted on AGVs) to ensure the arm remains steady while the vehicle is in motion.
Precision Steering
Essential for Ackerman or Swerve drive modules, allowing autonomous forklifts to execute complex maneuvers in narrow warehouse aisles.
Medical Transporters
Employed in hospital logistics robots where silence and smooth motion are critical to prevent disturbing patients or spilling sensitive fluids.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a cycloidal drive compare to a planetary gearbox?
Planetary gears are generally more affordable and sufficient for simple traction, but they suffer from backlash (play) which degrades accuracy over time. Cycloidal drives offer higher shock load resistance (500% vs 300%) and near-zero backlash, making them superior for precision positioning and frequent start-stop cycles.
Why is "Zero Backlash" critical for AGVs?
Backlash causes a "dead zone" when reversing direction. In AGVs using LIDAR or SLAM navigation, physical backlash translates to localization errors—the robot thinks it's in one spot, but the wheels haven't engaged yet. Zero backlash ensures the physical movement perfectly matches the software commands.
What reduction ratios are typical for cycloidal gears?
They offer very high ratios in a single stage, typically ranging from 30:1 up to 185:1 or higher. This eliminates the need for multi-stage gearboxes, saving axial space within the robot chassis and reducing the overall part count.
Are cycloidal gears backdrivable?
Generally, high-ratio cycloidal gears are difficult to backdrive. This is often a safety feature in robotics; if power is lost, the friction in the gear holds the load in place (like a parking brake), preventing the AGV from rolling down a ramp.
What kind of maintenance do they require?
Most cycloidal units for robotics come sealed and pre-lubricated with long-life grease. Because they operate on rolling contact rather than sliding friction, wear is minimal, and they often last the entire service life of the AGV (20,000+ hours) without maintenance.
How do they handle emergency stops?
Exceptionally well. The load is shared across many pins/teeth simultaneously. This design allows them to absorb momentary shock loads up to 5 times their rated nominal torque, making them immune to the teeth-shearing damage that plagues planetary gears during E-stops.
Are they heavier than harmonic drives?
Yes, cycloidal drives are typically heavier and more robust than harmonic (strain wave) drives. Harmonic drives are better for lightweight robotic arms, while cycloidal drives are preferred for the base/drivetrain of mobile robots where load capacity and stiffness are more important than weight.
Do they generate significant noise?
Modern precision cycloidal gears are very quiet due to the rolling contact mechanics and balanced eccentric masses. However, at very high input speeds, they can produce a distinct frequency. Proper mounting and housing design usually mitigate this effectively.
What is the efficiency loss?
Efficiency typically ranges from 85% to 95%, depending on the reduction ratio and lubrication viscosity. While slightly lower than a single-stage planetary gear, the trade-off for high torque density and zero backlash is generally considered negligible for AGV applications.
Can I mount a servo motor directly?
Yes, most commercial cycloidal units feature standardized flange adapters and clamping collars designed to accept shafts from common servo motor brands (Delta, Yaskawa, Panasonic, etc.) without custom machining.
How does temperature affect performance?
Rolling friction generates less heat than sliding friction, but thermal expansion can tighten clearances. High-quality units use matched thermal expansion materials. For extreme cold storage warehouses (-30°C), specific low-viscosity synthetic greases are required.
What is "Lost Motion" in this context?
Lost motion is similar to backlash but includes elastic deformation (springiness) of the gear under load. Cycloidal gears have very low lost motion (often <1 arcmin), meaning they are incredibly stiff and responsive, which is vital for precise path following.