CNC Machining
Precision meets autonomy. Discover how Computer Numerical Control (CNC) manufacturing creates the high-tolerance chassis, custom sensor housings, and durable drivetrain components essential for modern Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs).

Core Concepts
Subtractive Manufacturing
Unlike 3D printing, CNC removes material from a solid block to create parts with superior structural integrity, vital for heavy-payload AGVs.
Micron-Level Precision
Achieves extremely tight tolerances (±0.005mm) required for gearbox assembly, bearing fits, and precise wheel alignment in mobile robots.
Multi-Axis Control
Utilizing 3, 4, and 5-axis machines to cut complex geometries for omnidirectional wheels and intricate robotic manipulator joints.
Material Versatility
Capable of machining Aluminum 6061 for lightweight frames, stainless steel for hygiene, or Delrin for low-friction wear pads.
G-Code Automation
Translates CAD designs into machine coordinates, allowing for perfectly repeatable production of spare parts across your robot fleet.
Surface Finishing
Post-process anodizing or powder coating ensures CNC parts resist corrosion and electrical interference in harsh warehouse environments.
From CAD to Autonomous Reality
The journey of an AGV component begins in Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. Engineers design critical stress-bearing parts, such as the main chassis plate or the suspension arms. This data is converted into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) instructions.
The CNC machine uses high-speed rotating tools to carve the component from a solid block of raw material (stock). For robotics, this process is non-negotiable for parts that require high rigidity and perfect flatness for mounting LiDAR sensors and drive motors.
Unlike casting or welding, CNC machining introduces no thermal warping, ensuring that the kinematic models used by the robot's navigation software match the physical reality of the hardware to within micrometers.
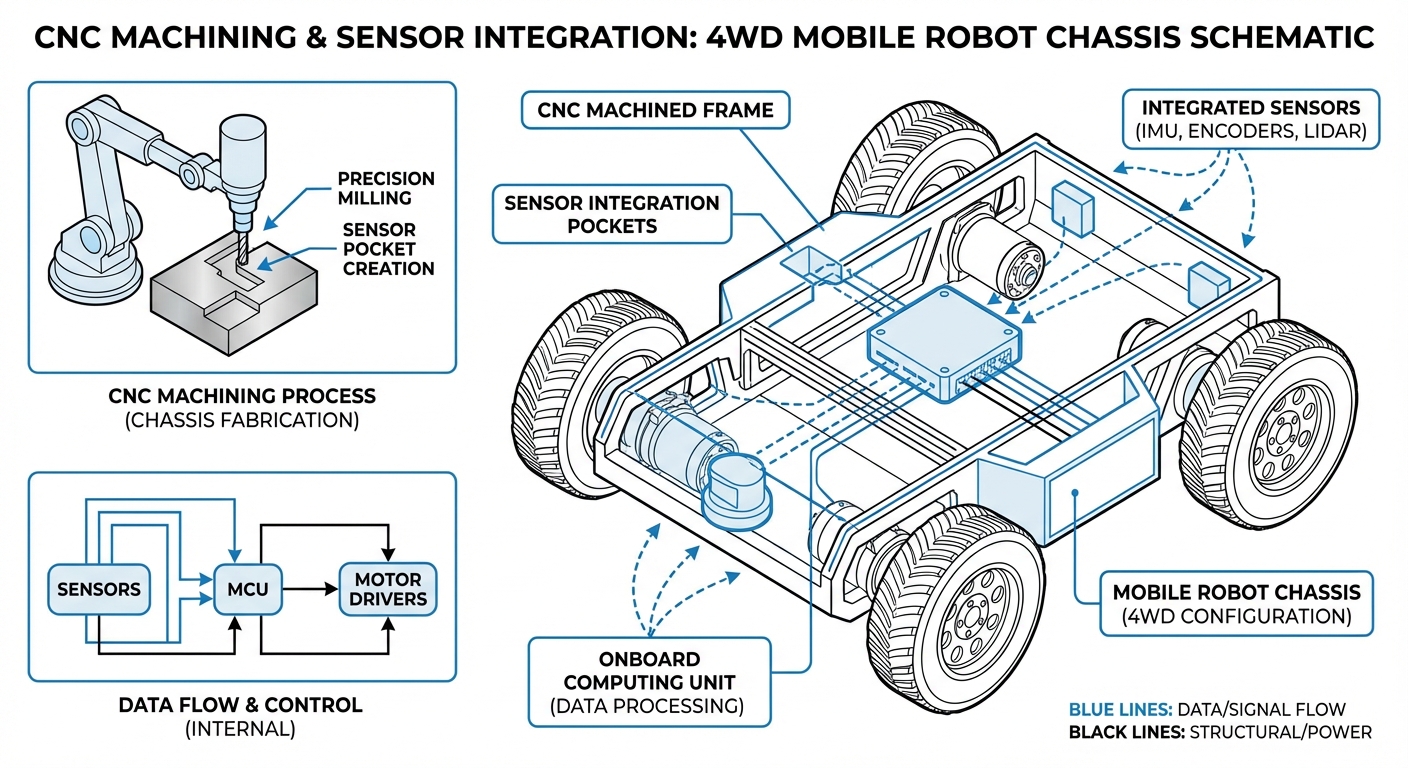
Real-World Applications in AGVs
Custom Chassis Fabrication
Machining unibody frames from aluminum billets to maximize strength-to-weight ratios for mobile robots requiring long battery life and high payload capacity.
LiDAR & Sensor Mounts
Creating rigid, vibration-dampened housings for sensitive navigation sensors. Precise machining ensures the sensor's viewing angle remains constant over time.
Drivetrain Components
Production of custom gearboxes, motor mounts, and wheel hubs that require H7 tolerance fits for bearings to ensure smooth, efficient motion control.
End-Effector Tooling
Rapid manufacturing of custom "hands" or lifting forks for AGVs, allowing a standard robot base to be adapted for specific tasks like pallet lifting or bin picking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why choose CNC machining over 3D printing for robot parts?
While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping, CNC machining offers superior isotropic strength and material properties. For load-bearing AGV chassis and drivetrain components, CNC machined metal prevents fatigue failure and handles significantly higher dynamic loads.
What is the best material for AGV chassis construction?
Aluminum 6061-T6 is the industry standard due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and machinability. For high-stress internal gears or axles, 4140 Steel or Stainless Steel 304 is often used, though it adds weight to the system.
Do I need 5-axis machining for my robot design?
Most AGV structural parts can be made on 3-axis machines. However, 5-axis machining is beneficial for complex, organic shapes—like omnidirectional wheel hubs or integrated sensor housings—reducing setup time and improving accuracy by machining multiple sides in one go.
How does CNC machining impact the cost of a robot fleet?
CNC has higher upfront setup costs compared to printing but is cheaper than injection molding for low-to-medium volumes (1-1000 units). For robotics fleets, the durability of CNC parts reduces long-term maintenance and replacement costs, offering better ROI.
What tolerances should I specify for bearing fits?
For standard rolling bearings in wheels or joints, an ISO tolerance of H7 (hole) and g6 (shaft) is common. Specifying tolerances tighter than necessary increases cost significantly, so only apply high precision to mating surfaces.
Can CNC machining handle plastic parts for robotics?
Absolutely. Engineering plastics like Delrin (Acetal), Nylon, and PEEK are frequently machined for AGVs. Delrin is particularly popular for gears and sliding wear pads because it is naturally self-lubricating and easy to machine.
How can I optimize my robot design for CNC (DFM)?
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) includes adding internal corner radii (since end mills are round), minimizing deep pockets, and designing parts that can be machined from as few orientations as possible to reduce setup time and cost.
What surface finishes are recommended for exposed AGV parts?
For aluminum, Type II Anodizing provides corrosion resistance and comes in various colors for branding. Bead blasting before anodizing hides machining marks. For steel parts, electroless nickel plating or black oxide are common to prevent rust.
How does CNC machining assist in thermal management?
AGV computers and motor drivers generate heat. CNC machining allows the creation of integrated heatsinks directly into the chassis body, using fin structures to dissipate heat efficiently without needing separate, bolted-on cooling units.
Is it possible to modify CNC parts after they are made?
Yes, unlike molded parts, metal CNC parts can be reworked. You can drill additional mounting holes or mill down surfaces if design requirements change, which is valuable during the iterative R&D phase of robot development.
What is the typical lead time for custom AGV parts?
Lead times vary by shop load and complexity. Simple 3-axis parts can often be turned around in 3-5 days. Complex, multi-axis components or large batch orders typically require 2-4 weeks, including time for material sourcing and finishing.
How does CNC machining ensure part consistency?
Once a G-code program is verified, the machine follows the exact same path every time. This repeatability ensures that if a suspension arm breaks on a robot in the field, a replacement part will fit perfectly without manual adjustment.