Construction Site Surveying
Automate the collection of high-fidelity topographic data and progress monitoring using autonomous mobile robots. By integrating LiDAR and RTK-GPS, this application delivers sub-centimeter accuracy for BIM integration, reducing rework and ensuring projects stay on schedule.

Why Automate Construction Site Surveying?
Enhanced Safety
Deploy robots into hazardous, unstable, or difficult-to-reach terrain, keeping human surveyors out of harm's way while gathering critical data.
Sub-Centimeter Accuracy
Utilize industrial-grade LiDAR and RTK-GPS to achieve precision that supersedes traditional manual surveying methods, eliminating data drift.
Rapid Data Acquisition
Scan thousands of square meters in minutes. Robots operate continuously without fatigue, drastically shortening the feedback loop between surveying and analysis.
Real-Time BIM Updates
Automatically feed scan data into Building Information Models (BIM) to visualize progress against the digital twin instantly.
Cost Reduction
Lower operational costs by reducing crew size requirements and preventing expensive rework caused by outdated or inaccurate site data.
Consistent Repeatability
Execute identical flight or walk paths daily to track changes over time with pixel-perfect historical comparison.
Workflow Integration
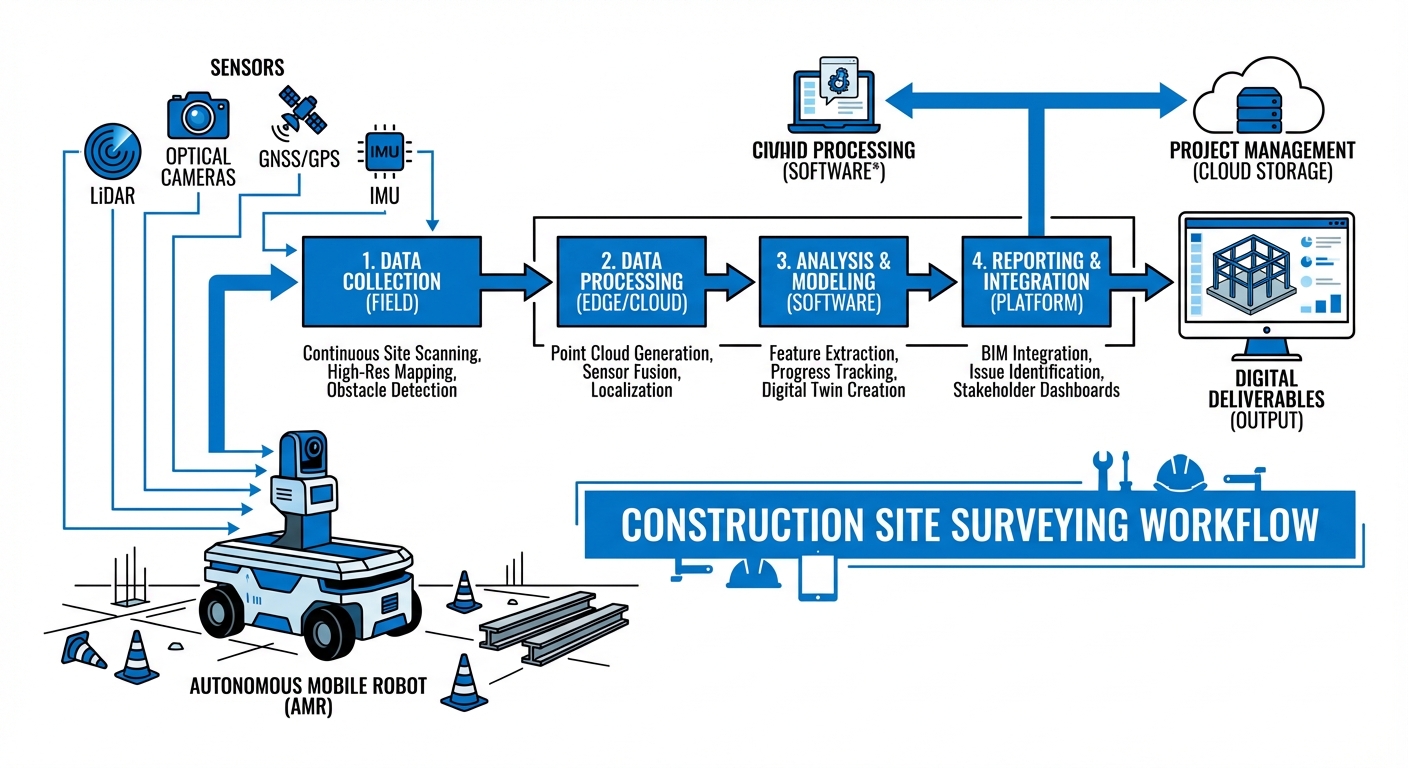
The robotic system utilizes a combination of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) and GNSS RTK to navigate complex construction environments autonomously. Before deployment, a rough boundary or waypoints are set via the fleet management software.
As the robot traverses the site, onboard LiDAR sensors capture millions of data points per second, generating dense point clouds. Concurrently, visual odometry cameras capture texture and color data to create photorealistic 3D maps.
Upon completion or during docking, data is uploaded to the edge server or cloud. Proprietary algorithms filter noise (such as moving workers or machinery) and align the new scan with the master BIM file, highlighting discrepancies for immediate review by site engineers.
Where It's Used
Commercial High-Rise
Monitoring floor flatness (FF/FL numbers), verifying structural column placement, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) installation validation against blueprints.
Civil Infrastructure
Surveying long-range corridors for highway construction, bridge inspection, and verifying earthwork volumes for cut-and-fill operations.
Mining & Excavation
Volumetric analysis of stockpiles, slope stability monitoring, and tunnel convergence measurements in underground environments.
Industrial Plant Retrofitting
Creating "as-built" digital twins of existing complex facilities to plan upgrades and clash detection for new machinery installation.
What You Need
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Robot Base | All-terrain UGV (Unmanned Ground Vehicle) or Quadruped capable of traversing gravel and debris. |
| Primary Sensor | 3D LiDAR (360° Field of View, min 100m range). |
| Localization | RTK-GPS Module for outdoor; Visual SLAM for indoor/GPS-denied areas. |
| Compute | Onboard edge computer (NVIDIA Jetson AGX or equivalent) for real-time point cloud registration. |
| Connectivity | 4G/5G LTE module or local mesh Wi-Fi for data telemetry. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the robot handle uneven terrain?
The application is designed for ruggedized tracked robots or quadruped systems (robot dogs) that can climb stairs, traverse gravel, and navigate obstacles up to 30cm in height.
What is the accuracy of the scan data?
With RTK-GPS enabled, absolute global accuracy is within 1-2 cm. Relative accuracy within the point cloud (measurement between two points in the scan) is typically ±2mm depending on the LiDAR specifications.
Does it work in the dark?
Yes. LiDAR is an active sensor that creates its own light source, allowing the robot to survey in complete darkness, tunnels, or poorly lit basements.
Can it detect moving objects?
The robot's navigation stack detects moving objects for collision avoidance. For surveying data, post-processing software filters out "ghosts" caused by moving workers or machinery to ensure a clean static map.
How long does the battery last?
Typical runtimes range from 2 to 4 hours depending on the payload and terrain. The system supports autonomous docking and hot-swappable batteries for continuous operation.
Is it compatible with Autodesk Revit?
Yes. The output data is exported in standard formats like .LAS, .PLY, or .E57, which can be directly imported into Autodesk Revit, Navisworks, and other BIM software.
Does it require internet connectivity?
The robot can operate fully offline to collect data. Connectivity is only required for real-time remote monitoring or cloud uploading. Data can be retrieved manually via USB/LAN if needed.
What happens if it rains?
Hardware options are available with IP55 or IP67 ratings, allowing operation in light to moderate rain. However, heavy rain can degrade LiDAR data quality due to refraction.
How much training is needed to operate?
The user interface is designed for non-roboticists. A typical site surveyor can be trained to plan missions, deploy the robot, and retrieve data in less than one day.
Can it replace human surveyors entirely?
It replaces the tedious task of data collection, allowing human surveyors to focus on data analysis, legal boundary verification, and complex decision-making tasks.
Ready to implement Construction Site Surveying?
Scale your operations and reduce project timelines with our autonomous solutions.
Explore Our Robots