Event Cameras
Supercharge your AGV's vision with bio-inspired neuromorphic tech. Unlike frame-based sensors, event cameras grab dynamics in microseconds for blazing nav and obstacle dodging in crazy lighting.

Core Concepts
Asynchronous Sensing
Pixels work solo, firing data only on intensity shifts. It apes biological retinas, cutting out the redundant processing that plagues frame cameras.
Microsecond Latency
Reaction times plummet. Event cameras deliver microsecond temporal resolution, so robots snap to fast-moving obstacles instantly.
High Dynamic Range
Dynamic range over 120dB means they thrive in pitch-black shadows or glaring sun—essential for warehouse loading docks.
Low Power & Bandwidth
Transmitting just scene changes slashes bandwidth, easing compute loads and stretching battery life on mobile robots.
No Motion Blur
No traditional exposure time delivers razor-sharp edges amid high-speed spins or vibes, keeping SLAM dead accurate.
Data Sparsity
Output's a sparse event stream, not dense matrices—enabling super-efficient algos that target only active image parts.
How It Works
Traditional cameras strobe snapshots at fixed rates (say, 30 fps), leaving blind spots and heaps of redundant data in static scenes.
Event cameras—or neuromorphic sensors—flip the script. Pixels self-adjust sampling on visual changes, emitting an "event" the instant log intensity crosses a threshold.
Each event packs pixel coords (x, y), timestamp (t), and polarity (p) of the change (brighter/darker). Result: a continuous, async stream capturing true scene dynamics with sub-millisecond precision.
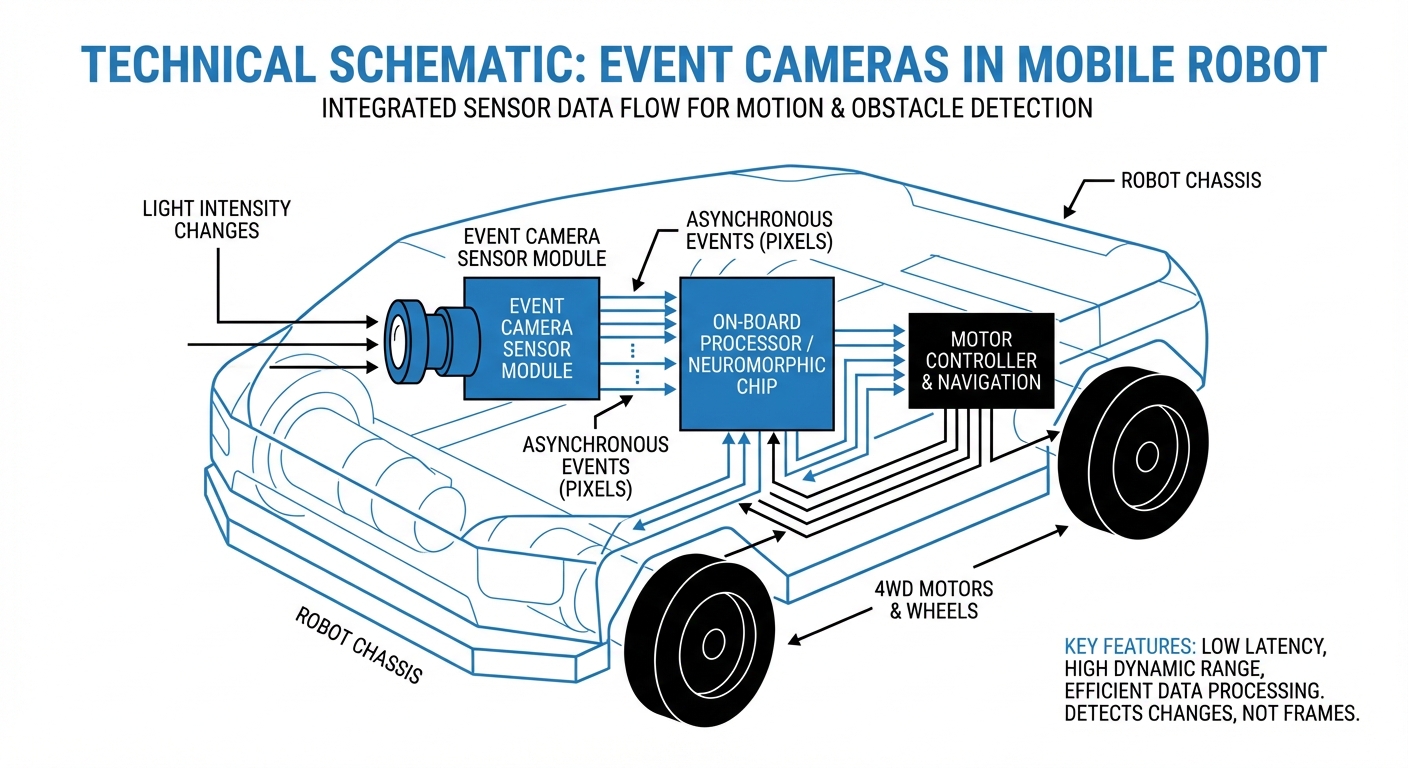
Real-World Applications
High-Speed Warehouse Logistics
Event-camera AGVs cruise aisles faster sans motion blur, nailing localization. They scan barcodes mid-flight and spot jutting obstacles instantly—throughput skyrockets.
Outdoor & Mixed-Light Navigation
Robots shifting from dim storage to bright bays blind standard cams. Event cameras glide through transitions, locking visual features for rock-solid SLAM.
Predictive Maintenance & Inspection
By catching high-freq vibrations invisible to eyes or standard cams, event vision spots micro-movements in gear, forecasting failures in belts or arms ahead of time.
Safety & Collision Avoidance
Ultra-low latency lets mobile robots detect and dodge falling objects or pedestrians in microseconds—key for human-robot collab spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does an event camera differ from a standard global shutter camera?
Standards snap full frames on a timer, inviting latency and blur. Events log pixel-level changes async for microsecond resolution and zero blur.
Why are event cameras better for high-speed AGVs?
High-speed AGVs battle blur-induced localization fails on standard sensors. Event cameras stream crisp edges at any velocity, keeping position locked and obstacles spotted—no slowdowns.
Can event cameras see in the dark?
They're killer in low light. Detecting relative changes—not absolute light—they run in near-dark (0.08 Lux) sans the noise plague of high-gain standards.
What happens if the AGV and scene are completely static?
If nothing at all is moving and the lighting stays perfectly steady, an event camera won't generate any data. But in robotics, those tiny micro-vibrations or the AGV's own subtle movements usually create enough events to paint a clear picture of the scene. You can also pair it with a regular frame camera to handle those totally static moments.
Do I need a GPU to handle event camera data?
Not at all. Since the data is super sparse—only capturing changes—the processing power needed is way lower than traditional frame-based video. Basic obstacle avoidance can even run on low-power microcontrollers, though intensive SLAM tasks might still love a bit of acceleration.
What is the data format output by these sensors?
The standard output is Address-Event Representation (AER)—a stream of tuples with (x, y, t, p), showing pixel coordinates, timestamp, and polarity of the brightness change.
Are there existing software libraries for integration?
Absolutely. Big manufacturers offer SDKs like Prophesee's Metavision, and there's solid support growing in ROS (Robot Operating System) with dedicated drivers and packages for event-based processing.
How does bandwidth usage compare to standard cameras?
Bandwidth varies a ton depending on the scene. In static spots, it's basically zero. In fast-action scenes, it ramps up, but overall, it's way lower than uncompressed video at the same temporal resolution.
Can event cameras replace LiDAR on my robot?
They're often the perfect sidekick rather than a full replacement. Event cameras crush it on speed and cost compared to 3D LiDAR, but LiDAR gives direct depth info. Combining them in sensor fusion creates the toughest navigation setup.
Is calibration difficult for event sensors?
Calibration can be tricky since standard checkerboards won't trigger events if you hold them still. You'll need special flashing patterns or keep moving the pattern to generate the data for solid intrinsic calibration.
What is the typical resolution of an event camera?
Resolutions tend to be lower than consumer cameras—usually QVGA (320x240) up to 720p HD (1280x720). But with their insane temporal resolution, that's plenty for most high-precision robotics jobs.
Are they cost-effective for mass production fleets?
Right now, they're pricier than standard CMOS sensors because of smaller production runs. But as automotive and mobile adoption surges, costs are plummeting, making them a smart pick for commercial AGV fleets.