Admittance Control
Bridge stiff automation and safe human teamwork. Admittance control turns outside forces into smooth, compliant moves, so AGVs can mingle naturally with people and their surroundings.

Core Concepts
Force Inputs
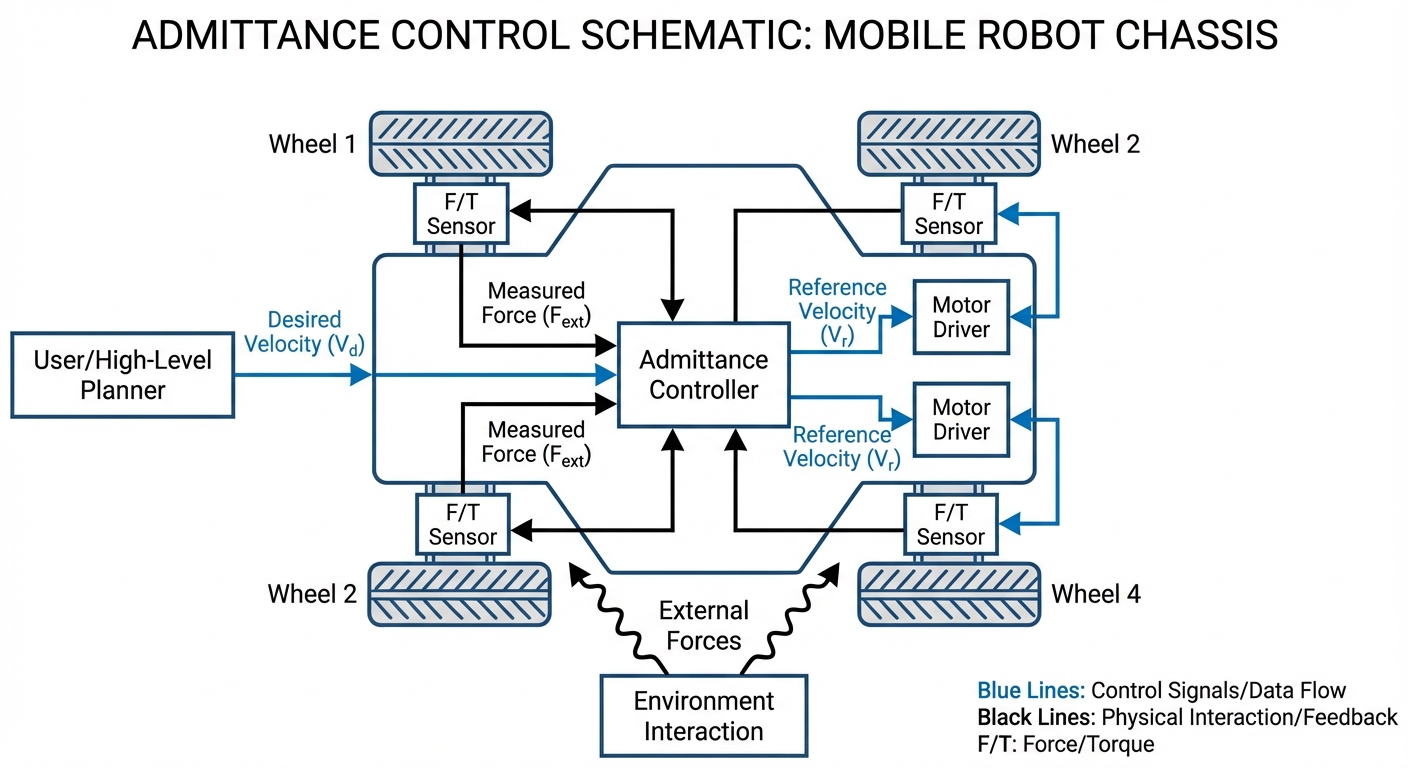
It senses forces on the robot chassis with force-torque sensors or motor current estimates—that becomes the main control signal.
Virtual Mass (Inertia)
Mimics the robot's real weight. Higher virtual mass makes the AGV feel hefty and slow to speed up, ironing out shaky pushes.
Virtual Damping
Like wading through honey for stability. It kills oscillations and makes sure the robot settles when you stop pushing.
Velocity Output
Unlike impedance control (which pumps out force), admittance control crunches the Mass-Spring-Damper model to spit out velocity paths.
Compliance
How much the robot yields to bumps or guiding hands. Crucial in shared spaces where robots and people mix.
Stability Control
Clever algorithms prevent runaway feedback in the virtual dynamics, keeping the robot steady even on tough contacts.
How It Works
Admittance control flips the usual mechanical interaction. Instead of forcing a spot and resisting, it measures the on it and figures how a virtual object would shift under them.
The math boils down to the Mass-Spring-Damper equation: .
The controller solves it live to create velocity commands. For instance, a human push hits the sensor, the admittance filter computes a velocity that flows the force, giving a light, power-steering feel.
Real-World Applications
Hand-Guiding & Teaching
Operators can just grab an AGV or mobile manipulator, guide it along a new route, and the robot logs the positions for easy replay—no coding required.
Heavy Payload Positioning
On assembly lines, workers tweak heavy chassis on AGVs with tiny pushes; admittance amps them up to shift tons effortlessly.
Crowded Navigation
In lively spots like hospitals, a bump into a person or obstacle? Admittance soaks the hit and stops or backs off instantly—no injuries.
Docking & Coupling
Docking to chargers or conveyors always has tiny offsets. Admittance gives the flex needed for a solid connection without wrecking plugs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Admittance and Impedance control?
It's all about cause-and-effect. Impedance tracks motion (position/velocity) and outputs force—great for light, backdrivable bots. Admittance tracks force and outputs motion (velocity/position)—perfect for heavy, stiff industrial AGVs.
What hardware is required to implement admittance control?
At minimum, estimate external forces. Best with a multi-axis Force-Torque (F/T) sensor on the chassis or handle. Or use motor currents, but friction makes it less precise.
Why is my robot oscillating or vibrating when touched?
Usually low virtual damping or laggy control loops. Crank up damping (D) or hit high loop speeds (>100Hz) to steady it out.
Can admittance control work on sloped surfaces?
Yes, but add gravity compensation. The model subtracts downhill gravity from sensor data; otherwise, it'll feel pulled and drift forever.
How does this impact the AGV's battery life?
Idle? Barely notices. Frequent hand-guiding? A tad more power draw, as motors react to unpredictable human nudges instead of optimized paths.
Is admittance control safe for ISO 3691-4 compliance?
Admittance is software, but pair it with safety hardware (PLd/Category 3) for standards. It cuts impact forces for safer ops, but the loop isn't safety-rated—keep scanners and e-stops.
What is "Virtual Stiffness" and when should I use it?
Virtual stiffness is like a spring pulling the robot back to center. Use it to resist shifts (say, holding steady while tightening a bolt) but still give under big forces.
How do I tune the Mass, Damping, and Stiffness parameters?
Kick off with high damping and mass for a safe, sluggish vibe. Ease down mass for lighter pushes, damping for longer glides. Tune damping to critically match stiffness—no overshoot.
Does this work with Mecanum or Omni-directional wheels?
Absolutely. It really shines on omni-directional bots, letting operators shove sideways or spin in place effortlessly, tapping full holonomic power.
What happens if the force sensor fails?
Drifty sensor? 'Ghost forces' make it wander. Solid setups add a deadman switch (enable button) on the handle—ignores inputs till you're actively guiding.
Can I combine this with autonomous navigation?
Yes. That's 'shared control'—robot follows its path, but you nudge it off-course (like dodging a surprise obstacle), blending inputs smoothly.
Is it expensive to add to an existing fleet?
Biggest hit: Force/Torque sensor at $2,000–$5,000 per bot. For basics, sensorless current estimation is just a software tweak—much cheaper.